Chmod 777 Command In Linux With Examples
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux Chmod 777 Issue 27 Xgqfrms Feiqa Github

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
CHMOD and CHOWN.

Chmod 777 command in linux with examples. Hi, I am trying to execute 'chmod 777 *.mp3', but I get an invalid option. $ chmod 777 sample.sh. The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources….
Before you see the chmod examples, I would strongly advise you to learn the basics of file permissions in Linux. However, this is a bad idea. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE….
Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System. Basically, it allows or disallows modifications of the file. Using chmod command will.
Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions:. Chmod Command using Operator Method. Chmod options mode file_name You can change permissions using alphanumeric characters (a+rwx) or with octal numbers (777).
Let’s play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu. # find / -type f -perm 0777 -print -exec chmod 644 {} \;. It works on *.MP3 but it does not work on *.mp3 root@lxp-cheung New Folder chmod command on linux.
Chmod 777 is one of those file control mechanisms. The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and the third 7 sets the permissions for everybody else. Find Files with 777 Permissions and Chmod to 644.
Others can read only". Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. CHOWN command explained with examples This is our second post in “Linux Files and folders” Series and first one is about chmod command in detail.
Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r. Make new files completely accessible (read, write, and execute) to absolutely everyone.
4 – To give Read Permission 2 – To give Write Permission 1 – To give Execute Permission. I used to work with linux command in the University and after a pause of few years… it brought me back to ‘beginers mode’ when I needed to use chmod. How to use chmod?.
This Linux chmod command tutorial shows you to change file permissions including mode, octal and binary of files and directories with examples and syntax. I was looking for some sites where I can find a comprehensive explanation with few examples. Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux’s chmod command.
Chmod command is used in two ways :. In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number. A step-by-step guide with Video Tutorials, Commands, Screenshots, Questions, Discussion forums on chmod Command in Linux with Examples | LinuxHelp | chmod command means change mode.chmod is used to alter the permission of files and folders.
It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and. Group can read only;. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments.
Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners. Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories. This tutorial explains CHMOD and CHOWN commands that are broadly used in Linux.
The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. You can change file permissions in this format:.
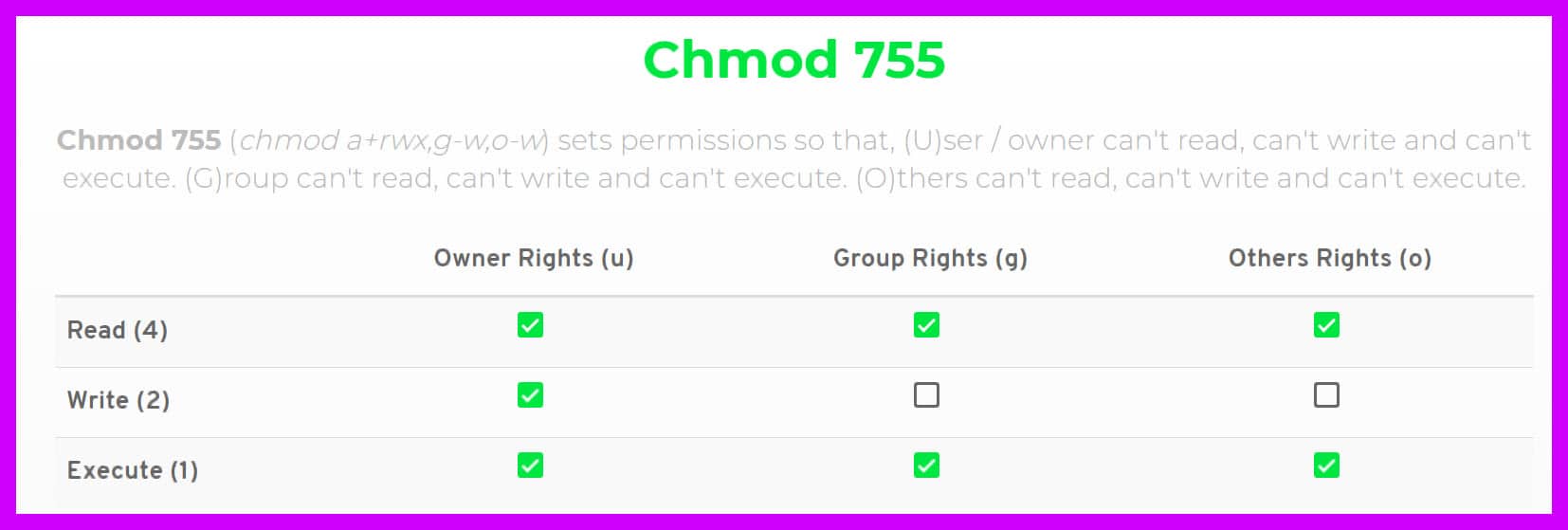
Chmod 775 / path / to /file Hopefully, this article can help you understand better about the file permissions in Unix system and the origin of the magical number “777”. The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory.The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory. 3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 + 2 + 1 = 7.
So if you want to recursively change the permission of all the files of example directory to 777 then you need to use chmod -R 777 example command as shown below. Root@localhost ~# chmod -v -R 777 example mode of ‘example’ retained as 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of ‘example/hello.rs’ changed from 0644 (rw-r--r--) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of ‘example/hello’ changed from 0755 (rwxr-xr-x) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx). This is equivalent to chmod 0777 aprsal:.
To remove write permission from orgcht:. As systems grew in number and types of users, access control lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility. Using octal value & position:.
We have already described the Linux file permissions. In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command. To set all permission bits on (anyone can read/write/execute):.
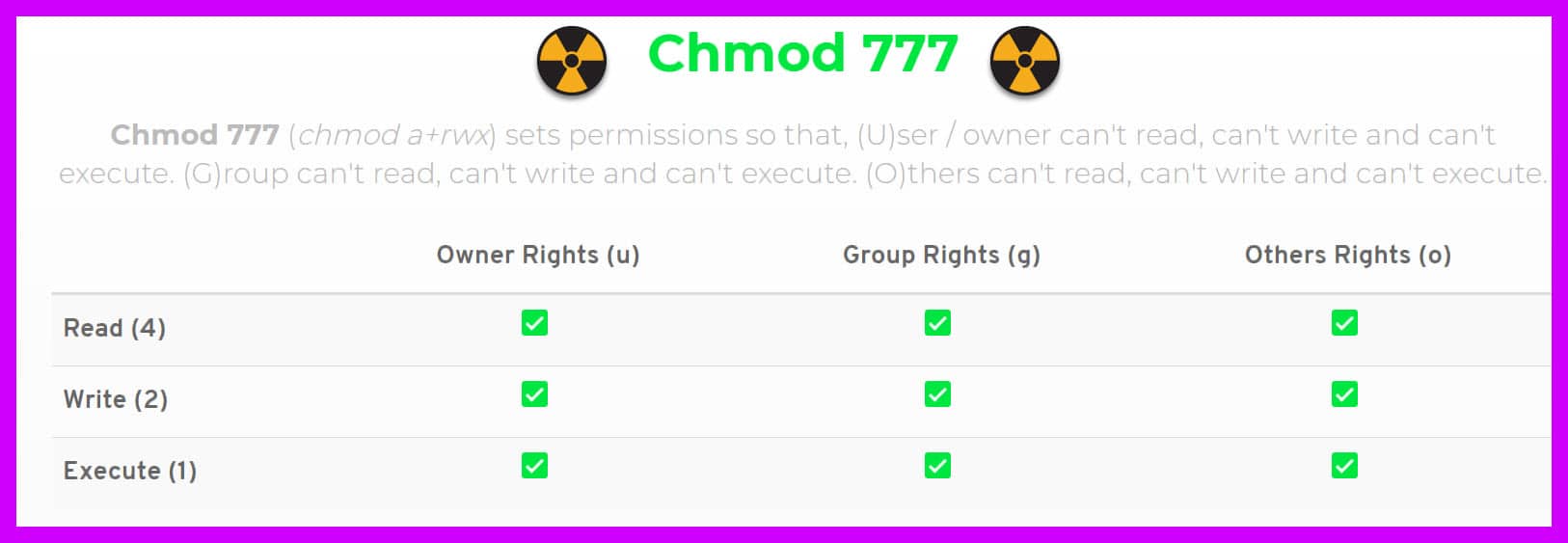
Never Use chmod 777 # Setting 777 permissions to a file or directory means that it will be readable, writable and executable by all users and may pose a huge security risk. Find all 777 permission directories and use chmod command to set permissions to 755. Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission.
What is chmod ?. The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linux-based operating systems. Chmod ( Change Mode ) is a command line utility in Unix , Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner , group and others.
How to use chmod?. To turn on read, write, and execute permissions, and turn off the set-user-ID bit, set-group-ID bit, and sticky bit attributes. Examples of chmod Command in Linux.
Csh — The C shell command. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules.
The chmod Linux command is used to change the access mode (aka file system permissions) of one or more files (or directories) only the owner or a privileged user may change the mode. Here’s a chmod. To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls -l command as shown below:.
In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command. Chmod command in Linux with examples Last Updated:. For example, for read and write permission, it is 4+2 = 6.
There are three basic modes to files and directories:. The number in the chmod command is an octal number, which is the sum of those free permissions, i.e. In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
FactorPad Linux Essentials playlist. User can read, write, and execute;. Chmod is a command used to change those file permissions and controls in terminals.
Find all 777 permission files and use chmod command to set permissions to 644. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they work.
The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system. Chmod 755 $(find /path/to/base/dir -type d) Both of these versions work nice as long as the number of files returned by the find command is small. CHOWN stands for CHange file OWNer and Group.
The command is relatively simple to use and involves using. The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permission. Let us take an example where a file test_file.txt has full permission to the owner, group and other.
Usually 777 is really 0777. Understanding the Linux systems helps make your system secure by restricting access to your files. In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command.
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. For my examples in this blog post I have created a directory called permissions containing several files, a directory and the usual system directories (.
The chmod command can be used with octals (as discussed in the Linux file permissions blog post) or symbolic representation. Examples chmod 644 file.htm. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;.
You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unix-like systems such as linux or BSD. Chmod -R 755 myfiles. Go into a folder, and run the ls -al command.
This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. Read, write and execute:.
To have combination of permissions, add required numbers. For example, if you recursively change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www directory to 777 , any user on the system will be able to create. $ chmod 777 file.txt (or) $ chmod ugo+rwx file.txt Give execute privilege to user.
The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. For Example, if you want to give Read & Write permission to User/Owner and Read permission to Group & Others using Alphabetical way then the command would be:. Make new files inaccessible to everyone - no one can read, write, or execute them.
Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. Chmod u+rw,g+r,o+r Filename Numerical Way :. Hey There, The 4th bit should be on most Linux and Unix OS's.
Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. The weird strings you see on each file line, like drwxr-xr-x, define the permissions of the file or folder. The chown command stands for “change owner” is used to change the owner.
In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. Second solution is to generate list of all files with find command and supply this list to the chmod command (as suggested by @lamgesh). Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for execute and.
Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.chmod stands for change mode.Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory. The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others.
More of a permission mechanism though. This is done with the chmod command. Linux Permissions are a great set of rules which.
Chown is a command to change the ownership of a file/folder or even multiple files/folders at a time to a specified user/group. Chmod has two operating modes:. The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode.
In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. To use this method you have to remember below Rules and Numbers for proper use. The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Chmod Linux Command & Examples. To check the options that are available in chmod, we can do by using Linux command:.
In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. 3 (1+2) — can execute and write 6 (2+4) — can write and read Examples:. Find Directories with 777 Permissions and Chmod to 755.
Linux File Permission :. Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system. Following are the examples of chmod commands in Linux explained in detail.
A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1.

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Give 777 Permission In All Subfolders In Htdocs Or Any Folder Ubuntu Youtube

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
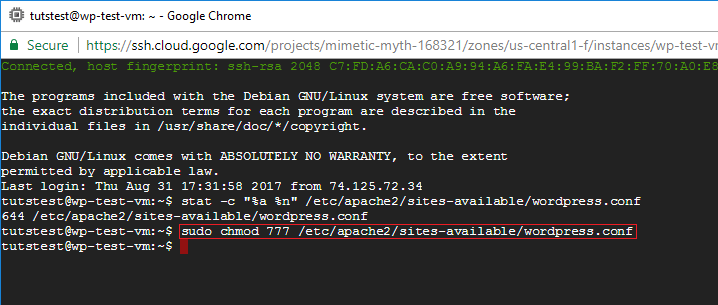
How To Fix Ftp Permission Errors On Google Cloud One Page Zen

Comandos Terminal Chmod 777 775 600 Youtube

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

How To Use Chmod 777 Command In Linux File Permissions How To Use Chmod Command Hindi Tutorial Youtube

Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Ms Tv Life Com

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Chmod 777 Comic Dzone Security

Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog
1

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
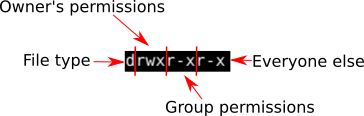
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples
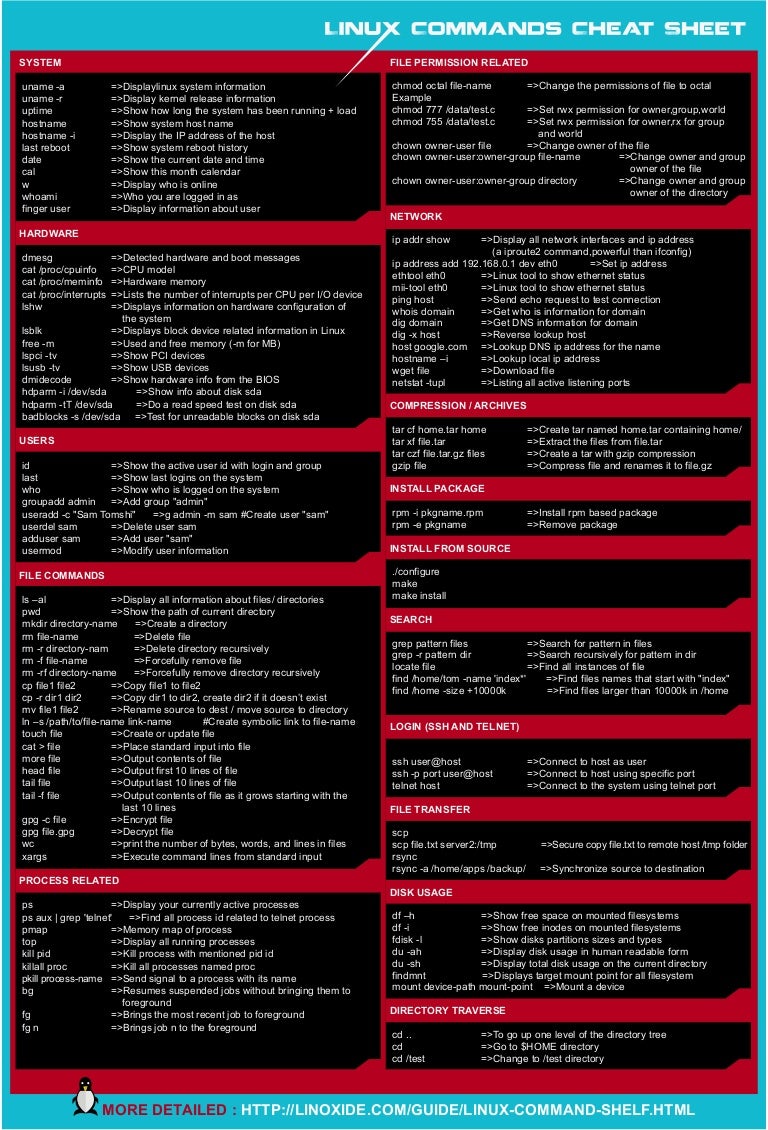
Linux Cheat Sheet

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

How To Set A File To This Drwxrwsrwx Permission On Ubuntu Stack Overflow

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download

Chmod Wikipedia

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

Posted Withrepost Terminalworld It Is The First Column In The Output Of Ls L Command Which Tells All About The Permissions Linux Software Engineer Topics

Chmod And Chown For Wordpress

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
How To Easily Back Up And Restore Linux File Permissions Linux Com
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

777 Chmod Unix File

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
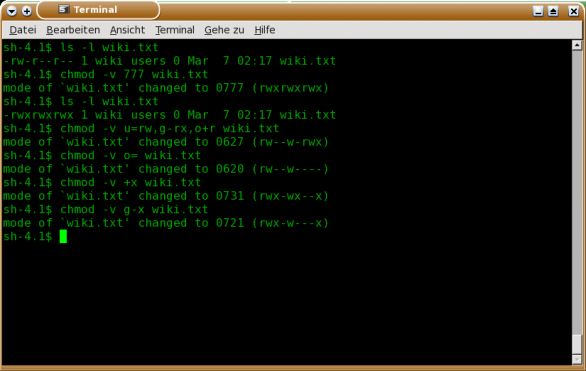
Chmod Shortcuts For Linux

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Means Linux Technology Theory Report

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
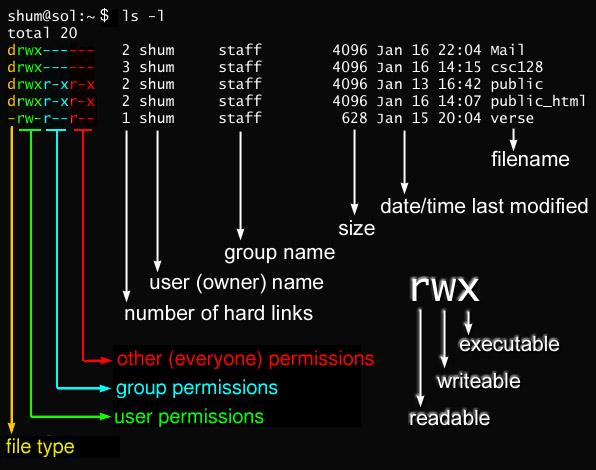
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Ownership And Permissions

The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought

Linux Commands Chmod

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
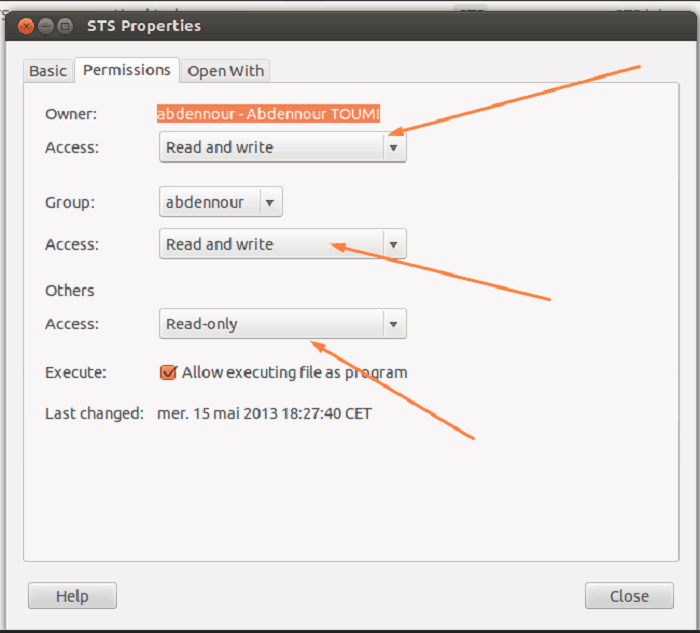
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Sudo Chmod 777 Opt

人気ダウンロード Chmod 777 Example ただの車

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
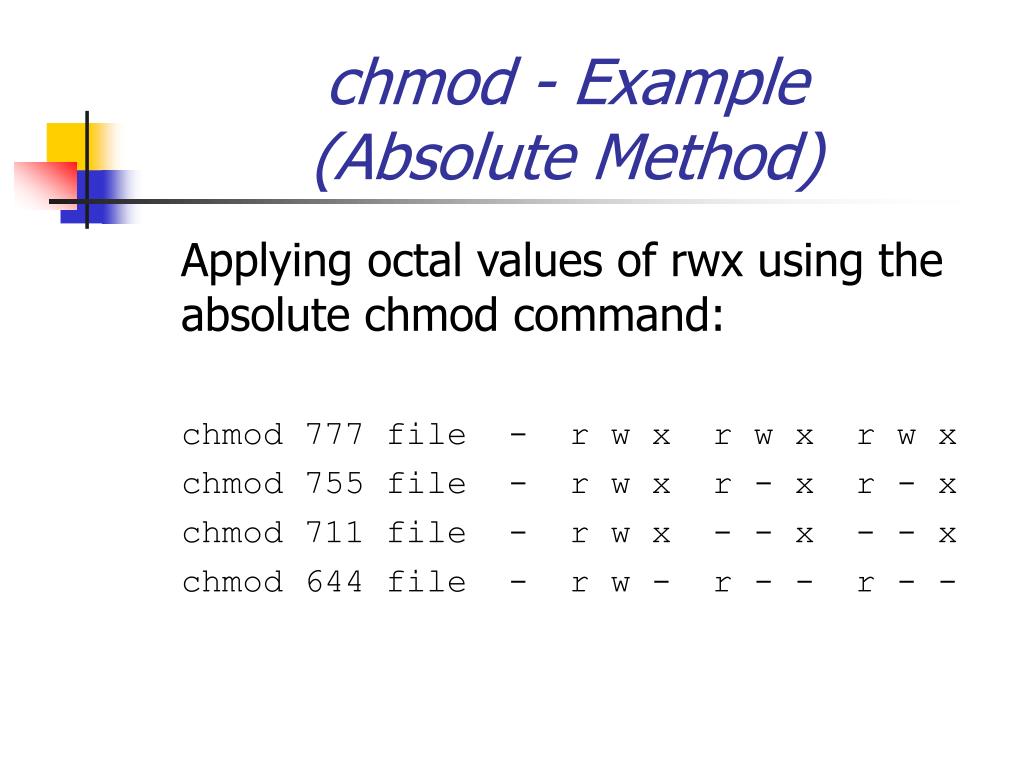
Chmod 777 Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples 01 12

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu
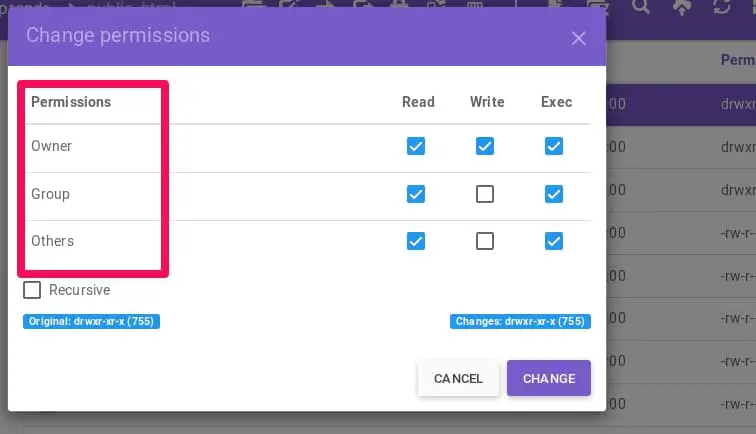
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Chmod 777 Allocating The Least By Amith Jayasekara Medium

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
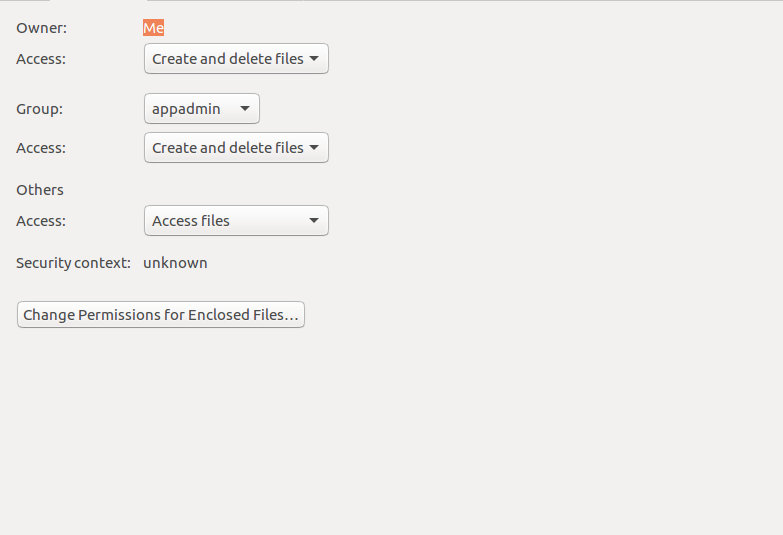
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Linux Chmod Tips

What Is Chmod 777

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

Ubuntu How Can I Chmod 777 All Subfolders Of Var Www Youtube
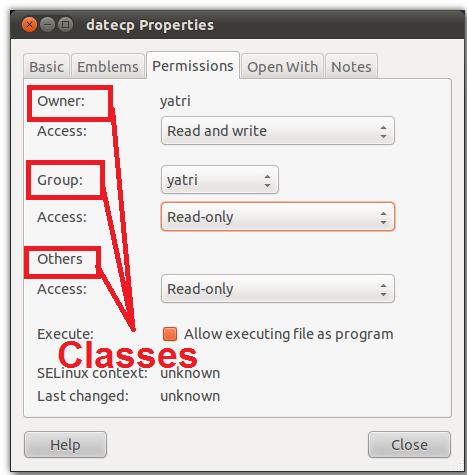
What Is Chmod 777
Cifs And Chmod 777 Ixsystems Community

Friendly Arm Mini2440 Setting Up A Nfs Server Alselectro

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux Chmod 777 Archives Ms Tv Life Com

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmtof5oge8os R2lzc9s8y8xkmcm3kyhtt M Kqujtci7flb3h Usqp Cau

Linux Unix Changing Permissions With Chmod Vinish Kapoor S Blog

Lock Your Private Folder In Ubuntu The Digi Life

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com
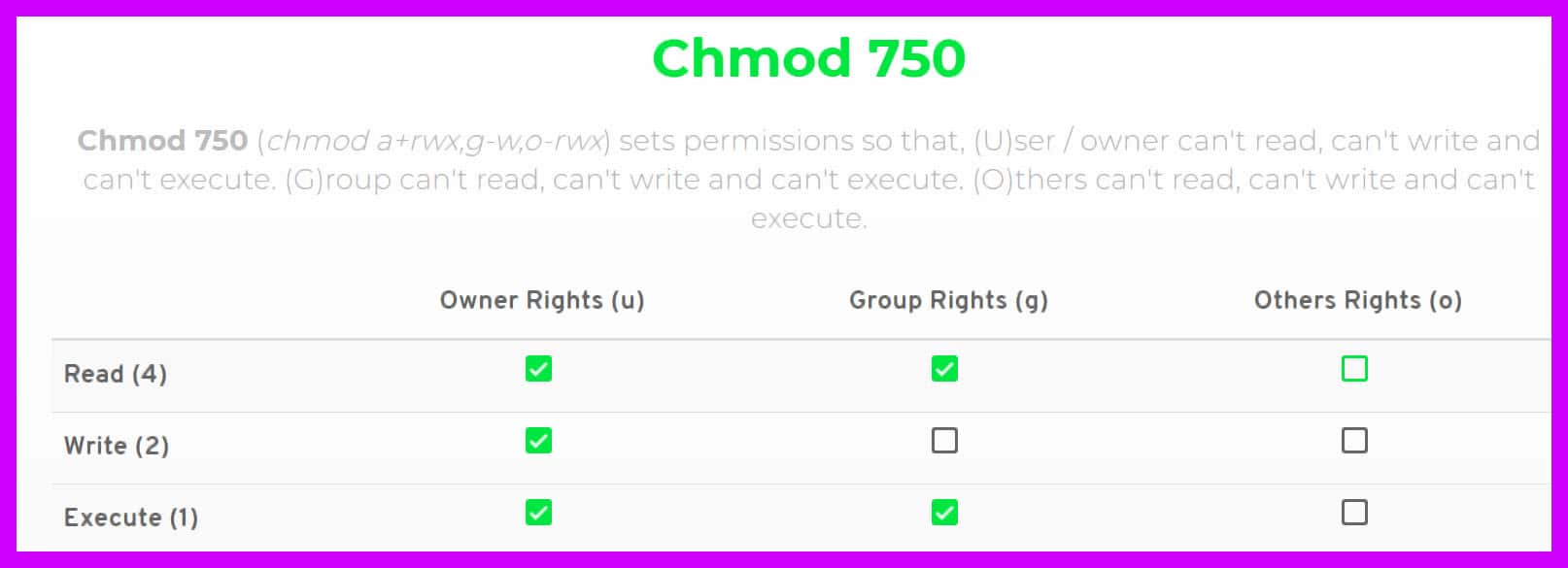
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

What Is Chmod 777 Poftut
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux
How To Share A Directory On A Linux Host On A Private Network With Another Linux Host On The Same Network Stfc Cloud Docs 1 0 Documentation
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
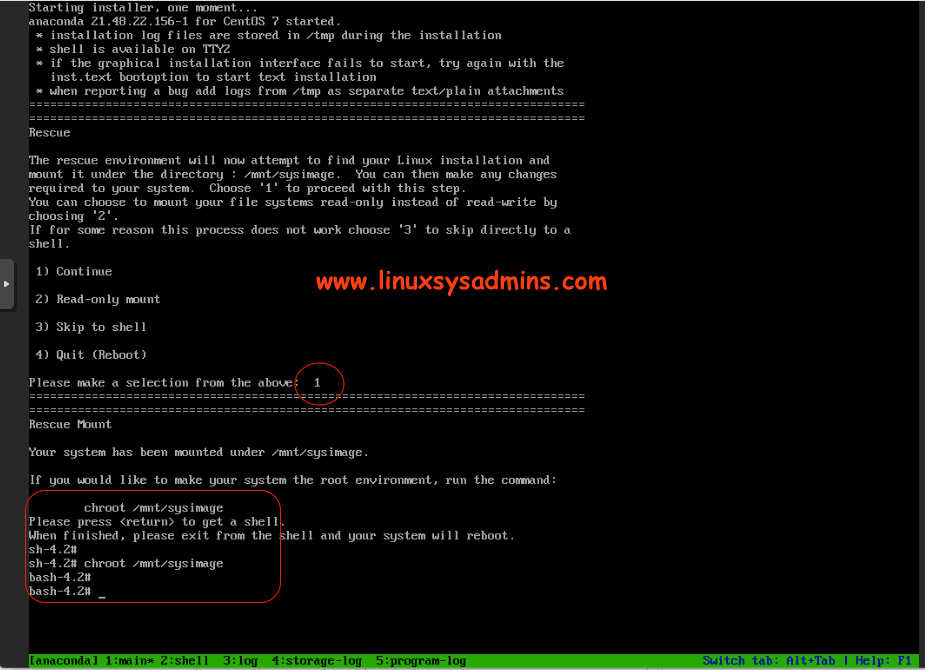
Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials



