Chmod Command In Linux Use
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought
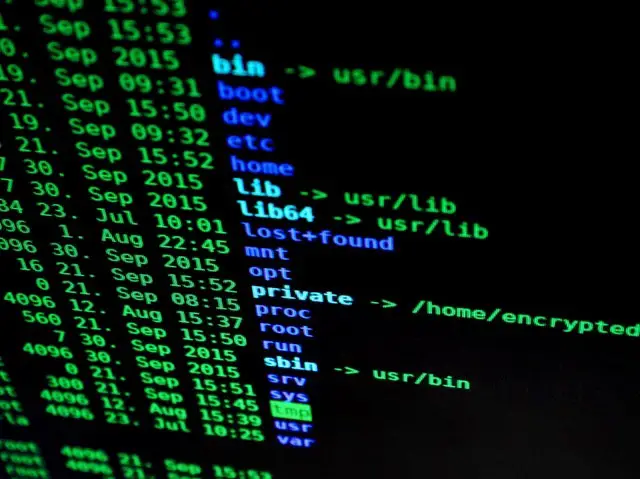
Linux grants three different types of permissions — read, write, and execute — for three different scopes:.

Chmod command in linux use. How to Use the chmod Command on Linux chmod Modifies File Permissions. The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons. Note the filenames are highlighted in red, which indicates the SUID bit is set.
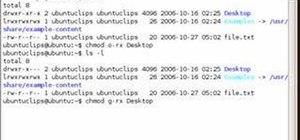
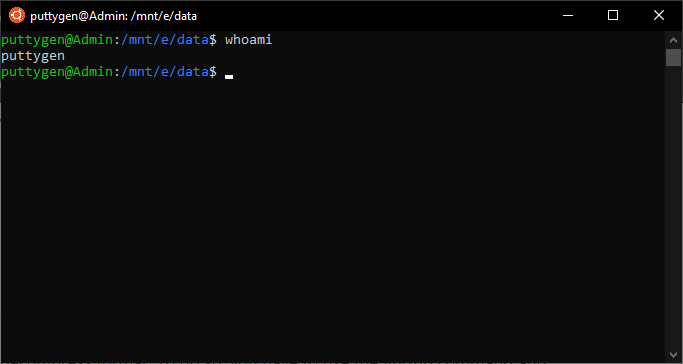
The chmod command is used to modify the permission types for files and directories. Chmod go-rx ~ As you can see, a + sign used with `chmod' adds accessibility and a - sign takes it away. The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions.
Once you create a new directory in Linux, then you can change permissions and create folders within the directory. Give the file’s owner read, write and execute permissions, read and execute permissions to group members. $ chmod u+x app.sh Change File Mode For Group.
Creating a Bash File. It is also used to change special mode flags. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
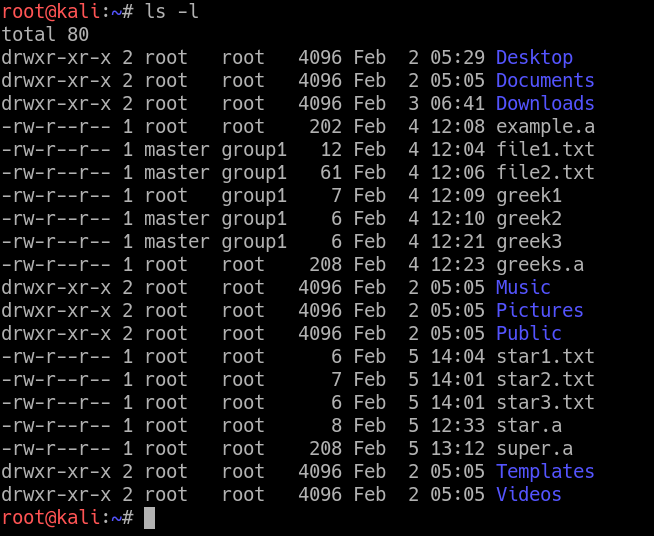
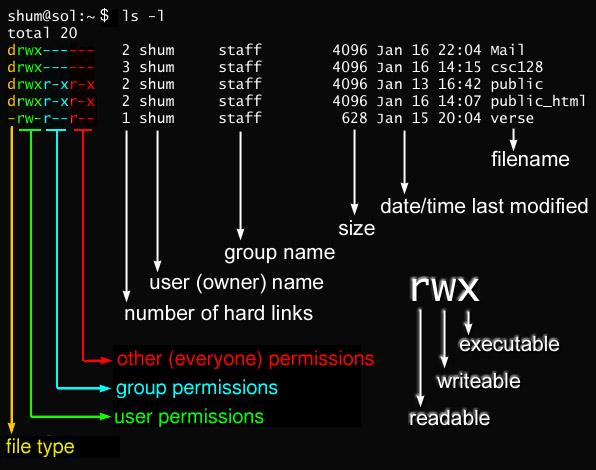
There are two methods by which we can change the permissions:. $ ls -l sample.sh -rwx-rw-r-- 1 matt deploy 94 Oct 4 03:12 sample.sh. Owner, group, and everyone.
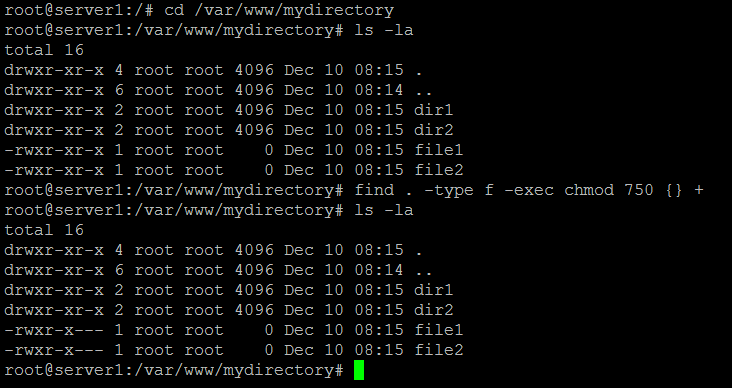
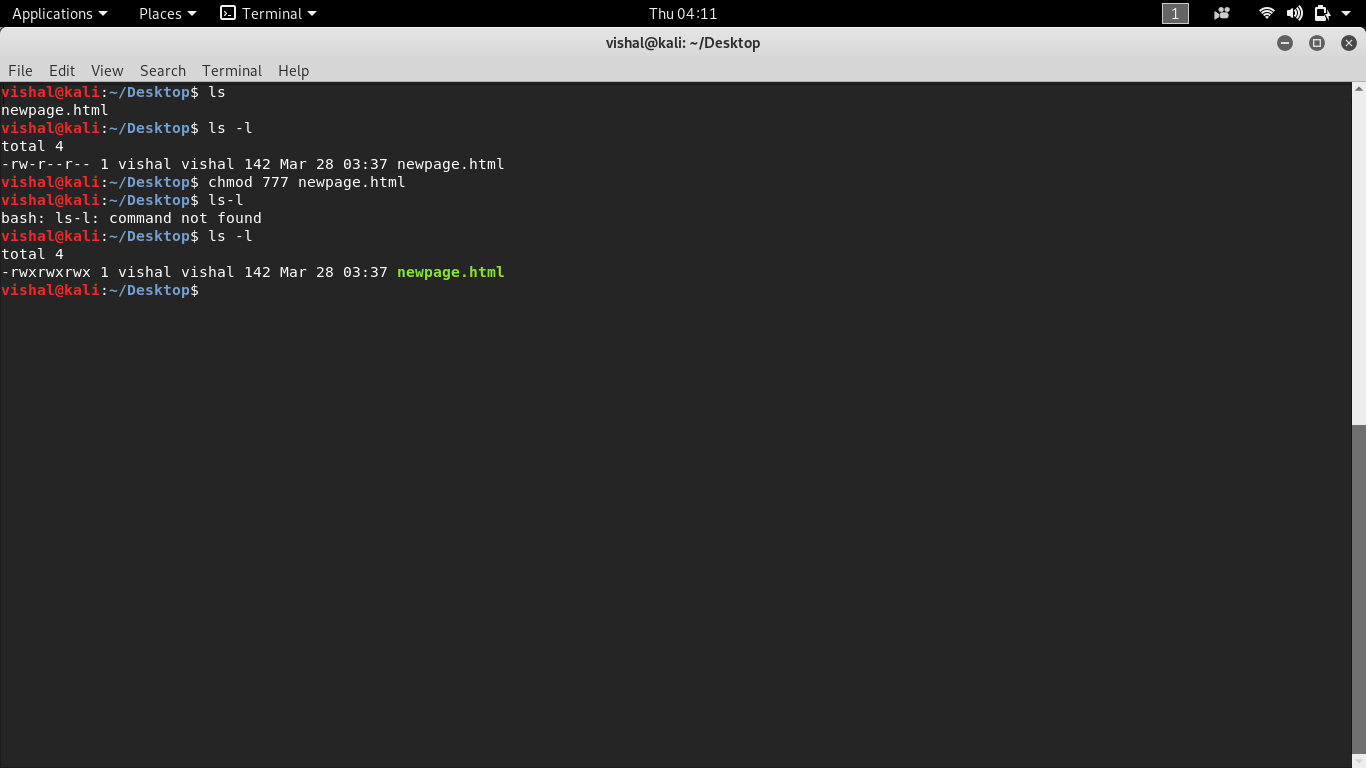
Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory. For a file codesudo chmod 777 file /codeFor a folder you need to use recursion codesudo chmod -R 777 folder /codeBreakdown:. In Linux/Unix like operating system, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file.
Below is a list of numerical permissions that can be set for the user, group, and everyone else on the. How‐ ever, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use chmod recursively and change file permission on Linux. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. This is not a prob‐ lem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. The Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files.
Chmod command accepts arguments in two notations;. Following is a sample of ls -l command output. We run the chmod command command to change file access permissions such as read, write, and access.
For detailed online information about the `chmod' command, enter. In our documentation of the umask command. Viewing and Understanding File Permissions.
After that, you will be able to run it without using the sh or bash commands. It is possible to use these features on directories of all levels and all files within those directories, individually or as a group. Chmod command in Linux with examples Last Updated:.
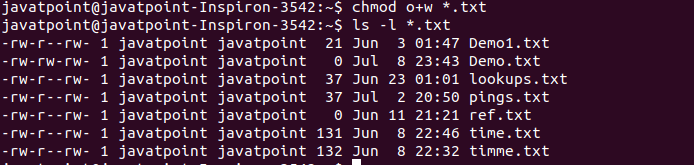
Chmod 775 file chmod 776 file chmod 777 file chmod 774READ MORE. Give the file’s owner read and write permissions and only read permissions to group members and all other users:. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux.
The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and. $ chmod u+X *. In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command.
Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system. The chmod command is also capable of changing the additional permissions or special modes of a file or directory. First, you should know what permissions a file has.
To use chmod, you need to know about access modes.Each file on a Linux system has nine access modes (or settings) that determine exactly who can. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. You can also create a directory and set permissions at the same time.
The weird strings you see on each file line, like drwxr-xr-x, define the permissions of the file or folder. The request is filtered by the umask. In general, chmod commands take the form:.
NDG Linux Essentials 2.0 Chapter 17 Exam Answers Which of the following commands set “other” permissions on file to r-x?. In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions. The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode.
The chmod command lets you change the permissions for a Linux file. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. It is used to change the permission for files and folders.
Go to file location using the cd command and then execute ls –l command. The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources…. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. Go into a folder, and run the ls -al command. For more information about file modes, see What Are File Permissions, And How Do They Work?.
Like verbose but report only when a change is made –reference= FILE :. In this tutorial, I am going through the steps to create a bash script and to make the script executable using the chmod command. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:.
Use FILE’s mode instead of MODE values – R :. You need to execute ls –l command. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person.
The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions.
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories). Chmod stands for “ Change Mode ” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command.
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. These permissions are given to file/folder to provide a secure environment to the OS, efficient management of a file and high-level access to the users accessing the files/ folders. The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linux-based operating systems.
If you ever need to say it out loud, just pronounce it exactly as it looks:. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. The name is an abbreviation of change mode.
How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command. To use the chmod command in Linux. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option.
Before explaining the syntax of the chmod command, you need to look at the cryptic way Linux reports file permissions. We can use g group before the plus in order to enable group execution right of the given file. In simple language, you can change the permissions of files and directories in Linux using chmod command.
Chmod has two operating modes:. Learn how to use the chmod command – the command for changing permissions on files. Edited Jun 10 ’11 at 19:57.
More Information on. The following are a few of the Linux commands that use the SUID bit to give the command elevated privileges when run by a regular user:. Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;.
In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users. Basic “chmod” Command examples in Linux. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode.
The symbolic modes use ' s ' to represent the setuid and setgid modes, and ' t ' to represent the sticky mode. This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. I know that I can use the stat command to check the Octal file level permission of each component and then use if-else to toggle the file permission, but is there any single line approach using find and xargs to first check what permission the file/directory has, and then use chmod to change it to 755 if it is set to something else.
Ls -l /bin/su ls -l /bin/ping ls -l /bin/mount ls -l /bin/umount ls -l /usr/bin/passwd. Others is special group which covers all users in a Linux system. How does chmod work?.
The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CH ange MOD e. Conclusion # You successfully learned how to use chmod command to set or change the file and directories permissions using either the symbolic or numeric mode.
However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. Linux Commands That Use SUID. Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions:.
The only tricky part is understanding that there are two ways to represent file permissions. The name speaks for itself. To create directories in Linux, you can open Terminal and use the command line with the mkdir command.
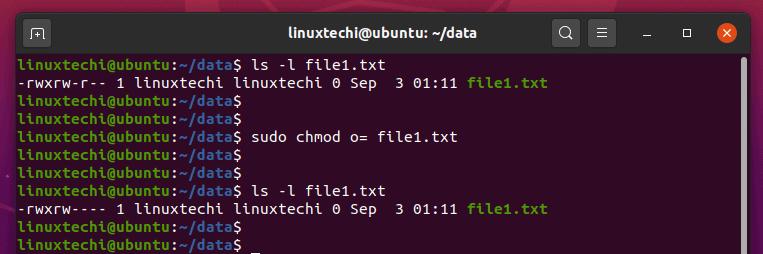
On a particular directory if you have multiple sub-directories and files, the following command will assign execute permission only to all the sub-directories in the current directory (not the files in the current directory). Chmod command in Linux -v :. Chmod o-r-w file chmod o+rx file chmod o=rx file chmod o=r+x file Which of the following commands sets “other” permissions on file to r-x?.
15-05-19 In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. We can use the -l (long format) option to have ls list the file permissions. Linux File Permission :.
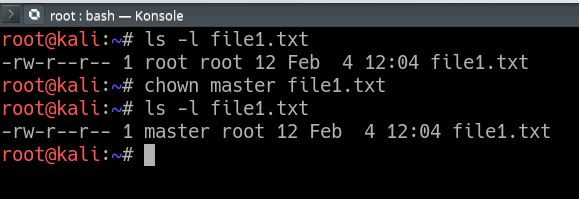
Use the chown command to change file owner and group information. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. Command chmod 666 means that all users will have read and write permissions.
It works identically for both files and directories. Here are some examples of how to use the chmod command in numeric mode:. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE….
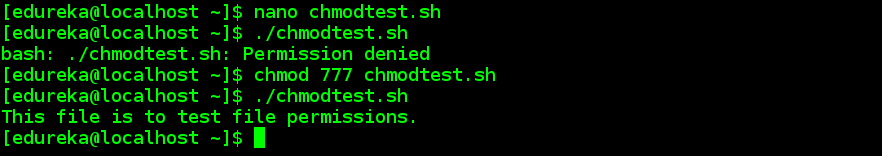
The command chmod can be followed by the “options” element which allows further options of the chmod command to be defined.The element “mode” represents the so-called umask that is applied to the “file” (which can also be a directory).This mask contains the information responsible for determining whether or not a user class should receive new access rights or be removed of the. It means same command is used to update the permission types for both files and directories. The first step is to create a new text file with .sh extension using the following command.
In this tutorial, we look at the chmod. The chmod command (abbreviated from change mode) is a Unix command that lets an operator tell the system how much (or little) access it should permit to a file. This page explains how to use chmod and chown command on Linux or Unix-like systems.
How to Use the chmod Command in Linux Command Syntax. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules.
It contains a comprehensive description of how to define and specify file permissions. It also allows to change the file permission recursively to configure multiple files and sub-directories using a single command. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions.
The modes are only applied to the appropriate classes, regardless of whether or not other classes are specified. We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file. Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories.
In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of. In this examples we will enable group execution of file app.sh $ chmod g+x app.sh Change File Mode For Other. Output a diagnostic for every file processed -c :.
Sudo - gives super user access to. It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and.

How To Run Sh File In Linux How To Use Linux

Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Executable How To Execute A Sh File Ask Ubuntu

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
How To Use The Chmod Terminal Command In Ubuntu Linux Operating Systems Wonderhowto

Command Line I Can T Change Mode For Some Directories Using Chmod Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Solved Problem 7 12 Points Answer The Following Questi Chegg Com

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Chmod 7777

Umask Wikipedia

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Designlinux
Top 50 Linux Commands With Example

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Tree Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Commands Chmod

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux Permissions Posix Chmod Chown Chgrp Youtube

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Copy Files Using The Install Command On Linux

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

File Permissions Linuxhowto Net

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Some Helpful Linux Commands Recently For A Coding Challenge I Was By Kate Schlunz Medium

Quick Answer How To Run Executable File In Linux Os Today

Linux Chmod Command Dracula Servers Tutorials

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chown And Chmod Command Usage In Linux System Develop Paper
Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example

Linux File System Permissions Using Chmod Command Linux Tutorial 19 Youtube
Linux Commands Most Important Linux Commands Edureka

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
How Do Linux Permissions Work
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
1

Whatever You Knew About Chmod Is Wrong Alien Coders

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Chmod Wikipedia
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Lock Usb Devices With Chmod Command In Linux Tutorials

How To Run A Script In Linux Nixcraft

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use The Chmod Terminal Command In Ubuntu Linux Operating Systems Wonderhowto

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
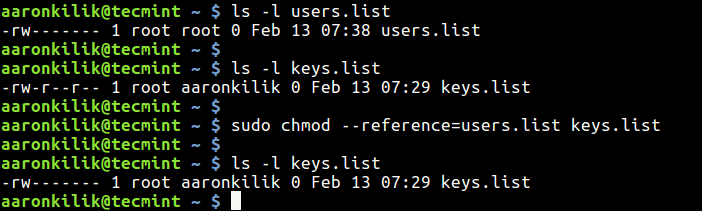
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
Lab 4 Manuel Montiel S Eportfolio
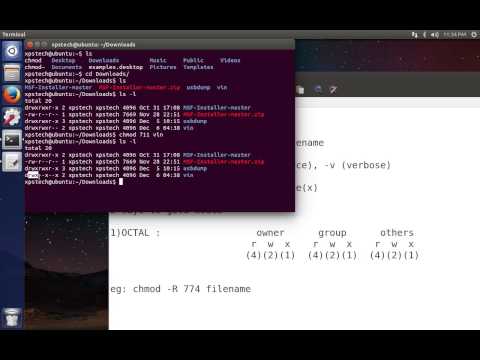
Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube
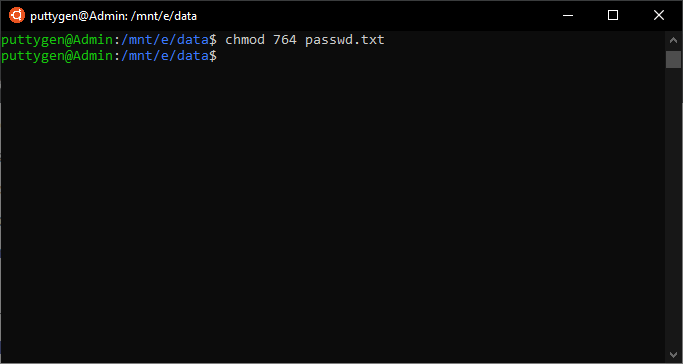
Top 50 Linux Commands With Example

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



