Chmod Numbers Explained
Linux File Folder Permissions

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

File Permissions Operating Systems I Ppt Download

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
If you like this article, then just share it.

Chmod numbers explained. ServerMania offers a variety of Hybrid, Cloud, and Dedicated Linux servers which all make use of the chmod command. The chmod command with the -R options allows you to recursively change the file’s permissions. The first chmod number is the owner permission;.
Up to this point, we’ve been setting the mode with letters. Exercises about the sticky bit included. To learn more use our calculator and read the references below at the bottom of this page.
Chmod is explained in most linuxes using man chmod. To quote the man chmod:. There are two ways to modify permissions, with numbers or with letters.
I know S denotes stick bit i tried to creat a directory and modify by chmod as chmod 7755 XXXX but no result. All of them are listed in man chmod, but I will type them out here as well. All, As first i searched in google but no result.
And finally, make it so anyone in the same group can ready/write and execute directories/files in the web root. You can use rwx format, but the simplest way is the number system. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others.
In symbolic mode, owners are denoted with the following symbols:. I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r. Chmod 0 file - Write by group chmod 002 file - Write by world chmod 100 file - execute by owner chmod 010 file - execute by group chmod 001 file - execute by world.
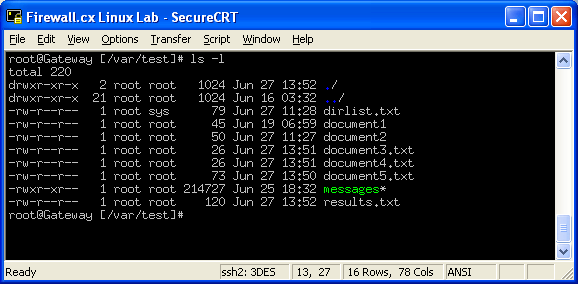
What is the chmod command?. Adding the numbers in each section results in permissions of 664. Chmod all files to 644;.
To combine these, just add the numbers together:. Column:3 is the user who owns the File/directory Column:4 Group to which file/directory belongs, all users in the group will have the mentioned permission. U = user owner.
This is where you can use the symbolic mode with chmod command. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits. The chmod command is used to modify the permission types for files and directories.
$ chmod -R go-rwx /var/www. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. R is for read permission, w is for write permission, x is for execute permission.
The problem with the absolute mode is that you should always provide three numbers for all the three owners even if you want to change the permission set for just one owner. It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and. And = causes them to be.
You will need to include the binary permissions for each of the three permission groups. For example chmod 751 sets this way:. Here are some of the commonly used permissions:.
The second chmod number is the group permission;. Here's an example using the testfile. The command to use when modifying permissions is chmod.
The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. So to set a file to permissions on file1 to read _rwxr_____, you would enter chmod 740 file1.
I am assuming you don't want the binary codes, though I quite like them, so here are the text codes:. Using letters is easier to understand for most people. It’s a frequently used command, so it’s important that any system admin knows how to use it.
Make a script executable. I'll start with some simple examples, then add some more details as we go along. Also i searched in the forum as well.
The difference is what permissions get set and which mode you use to set them. To set permissions, you will use the chmod command. It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically.
The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. That’s all, In this article, we have explained Linux SUID, SGID and Sticky Bit Concept Explained with Examples. Following are few examples on how to use the symbolic representation on chmod.
To use this method you have to remember below rules and alphabets for proper use. The third chmod number is the other’s permission. Number 1 means that you grant execute rights, number 2 means that you make the file writeable, number 4 means that you make the file readable.
U = user g = group o = other (not user or group) a = all + = add permissions - = remove permissions r = read w = write x = execute t = sticky bit. A compiled list of 30 exercises about linux permissions, the binary system, chmod, chgrp and chown. Write the permissions you want the file to have.
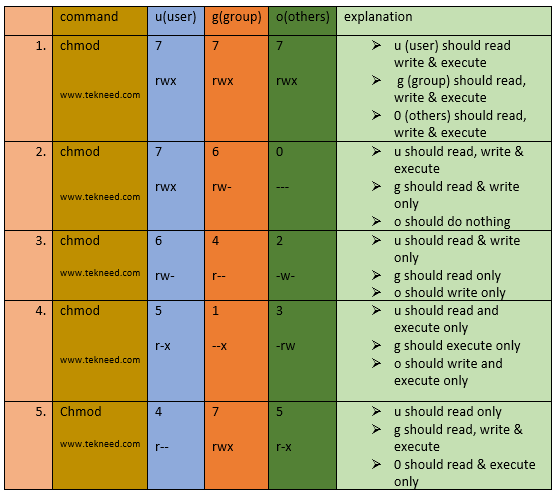
The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others. R stand for read .its value is 4. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.
The owner of the file/directory can read and. Suid, sgid and “sticky” (see below). Rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats.
Ugoa +-= perms. What is chmod, how is it used, and what things to avoid. This video attempts to explain what the "chmod" numbers mean that are often used but never explained in guides and installation instructions.
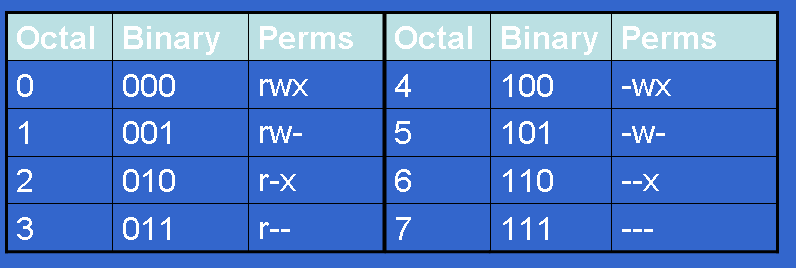
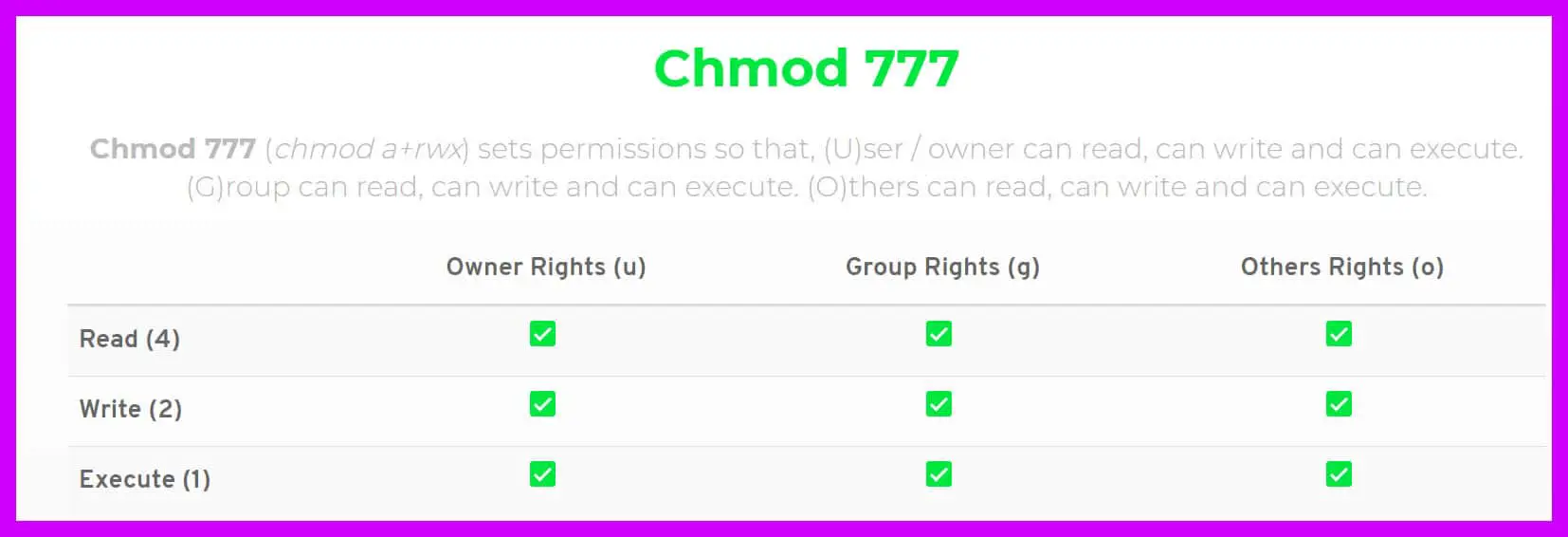
So for a file with ‘777’ permission, everyone can read, write and execute the file. Chmod 0777 is used to set all the permissions in one chmod execution, rather than combining changes with u+ etc. That looks like this:.
Chmod all directories with directory listing (.htaccess Options +Indexes) to 755;. You can either use numeric (Number based) or symbolic (Letter based) notation to define your permissions with this command. The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources….
Add up these numbers to specify needed rights. Below is the command's general structure:. This is done with the chmod command.
$ chmod -R g+rwx /var/www. W stand for the write.its value is 2. Chmod all .htaccess files to 644 chmod all robots.txt files to 644;.
What is the chmod command?. It means same command is used to update the permission types for both files and directories. Here's a summary that I have gathered.
We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. Chmod by the Numbers. Numerical Shorthand Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a three-digit number.
I hope you enjoy this article. With the chmod command, there are two different notations that you can utilize to specify the permissions that you want to set. Chmod all directories to 711;.
Both Octal and symbolic modes. The chmod command is commonly used to make a file "executable", like this:. Chmod stand for the:.
An alternative option to specifying the above is to use the 3 digit octal number method (e.g 755), remember the following:. The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file. Chmod Calculator Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers.
Sooner or later in the Linux world, you will have to change the permission on a file or directory. The chmod command name stands for "change mode", and as that name implies, the chmod command is used to change the mode of Unix/Linux files. This is known as symbolic mode.
And 775 means you are giving the permission to the file. Linux File Permissions Explained :. The operator + causes the selected file mode bits to be added to the existing file mode bits of each file;.
I am having a directory with permision drwxrwsr-x i want to create a new directory with same permision. 755 – This set of permission is commonly used in web server. You can also read more about modes on Unix systems with 'man 1 chmod' and 'man 2 chmod'.
The command takes the general form:. I actually give group write permissions as well, for users which need to modify content, such as users used to deploy code. It works identically for both files and directories.
Chmod command accepts arguments in two notations;. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. The format of a symbolic mode is:.
07-08-19 As explained in the article Permissions in Linux, Linux uses a combination of bits to store the permissions of a file. Here is another way to look at how we come to that number:-(rw-) (rw-) (r--) -(42-) (42-) (4--) 6 6 4. To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal.
Chmod changes the file mode of each specified FILE according to MODE, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Here’s how it works:. This video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change mode.
Well, the first digit is assigned to the Owner, the second digit is assigned to the Group and the third digit is assigned to the Others. $ chmod -R g+rx /var/www. There are two ways to represent the MODE:.
For user, it has read-write-execute. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE…. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments.
Chmod 444 file - Allow read permission to owner and group and world chmod 777 file - Allow everyone to read, write, and execute. The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner. We can change the permissions using the chmod command, which essentially changes the ‘r’, ‘w’ and ‘x’ characters associated with the file.
Chmod all directories that users can upload files to, to 755 (ex:. When modifying permissions be careful not to create security problems. Root@ip-10-12-2-217:/usr/bin# chmod g+x chage root@ip-10-12-2-217:/usr/bin# ls -l chage -rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow Jul 15 15 chage How to find all files in linux with SGID configured?.
There are two ways to use chmod:. 777) or symbolic notation (e.g. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules.
The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. Column:2 tells about the number of links or directories in the directory.
Each of the four digits is an octal value representing a set of permissions:. For example, to add execute. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command. In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. X stand for the execute.i.
Using the numbering scheme, the chmod command has three number places, for example 744, representing the three user types. WELL this is a command to change the permission of a file. - causes them to be removed;.
The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CH ange MOD e. Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
In this article, we’re going to cover;. The chmod command is used to change the various permission bits of a file or directory. You add the numbers to get the integer/number representing the permissions you wish to set.
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. It turns out that you can also set the mode numerically.
Using symbolic modes (letters to indicate the categories and permission) Using numeric modes (An octal (base 8) number that represents the mode). To make your life easier, write the permissions grouped into sets of three letters. Some files are configured to have very restrictive permissions to prevent unauthorized access.
To learn more use our calculator and read the references below at the bottom of this page. With chmod +x you set the executable bit for all - the owner, the owner group, and the other users. To recursively set permissions of files based on their type, use chmod in combination with the find command.
The first number on the left side is for "user", the middle one is for "group" and the right hand one. Chmod o-t /database/ # Remove Sticky Bit Alphabetically chmod 0777 /database # Remove Sticky Bit Numerically. Using chmod in symbolic mode.
Yes, I did call it "decimal notation", this is. Following are the symbolic representation of three different permissions:. You can use the below find command to search for all the files in Linux operating system, with SGID bit configured.
The middle digit represents the permissions for the group members. Chmod permission number explained.

Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

File Permissions How To Use Chmod Command Youtube

Linux Users And Groups Linode
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
Controlling File Permissions With Umask
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
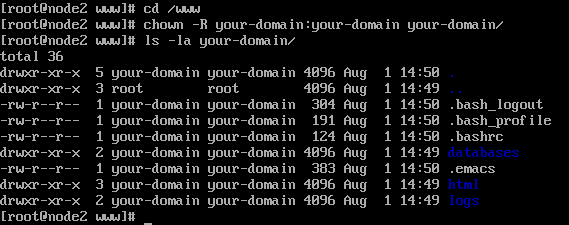
Chown Command In Linux Unix Explained With Examples The Linux Juggernaut

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

File Permissions Operating Systems I Ppt Download

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

08 What The Chmod Numbers Mean Youtube

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Chmod Fu By Red Shark Ab

Hot Linux File Permissions Explained Chmod Part 1 Peatix

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Extropia Tutorials Introduction To Unix For Web Technicians The Chmod Utility

How To Use The Terminal Chmod Command Demystified And Put To Use Youtube
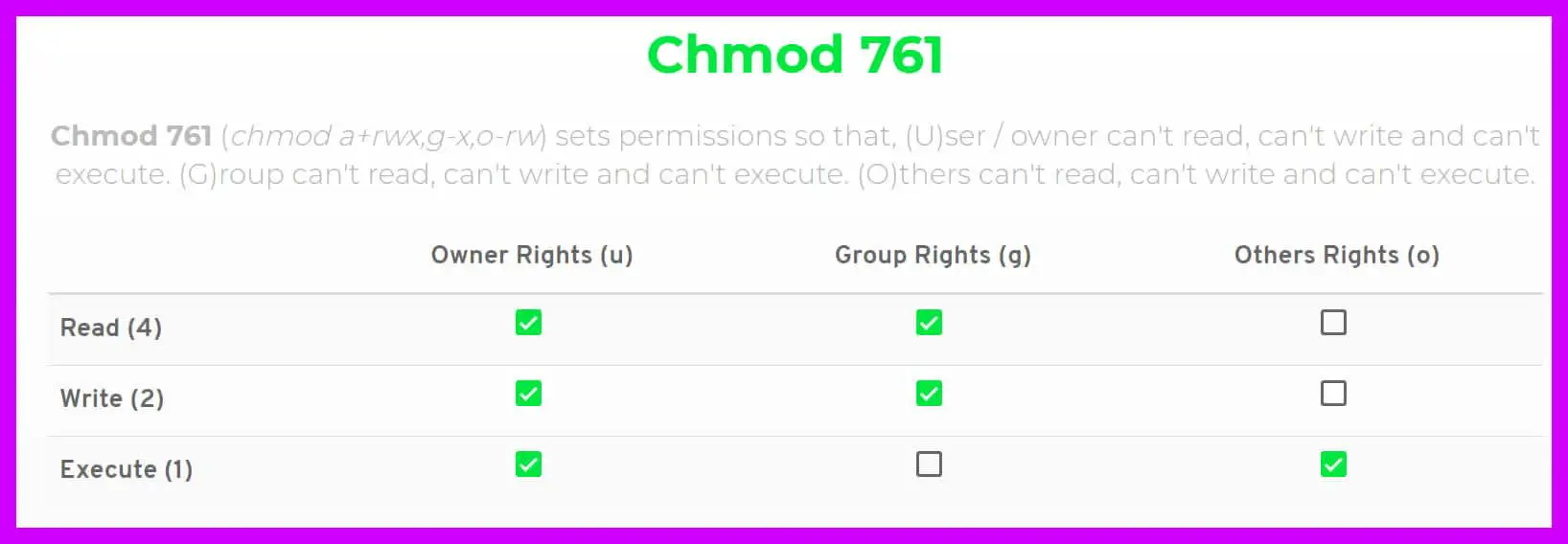
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Unix Permissions Explained

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Linux Users And Groups Linode
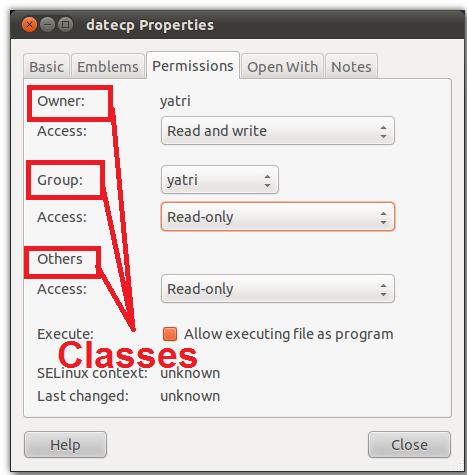
What Is Chmod 777
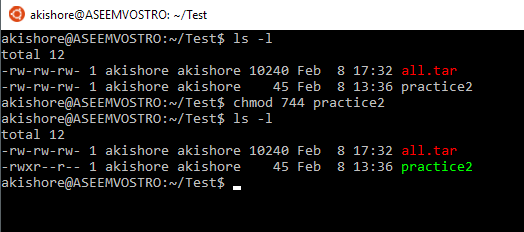
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Umask Wikipedia

Chmod Wikipedia

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
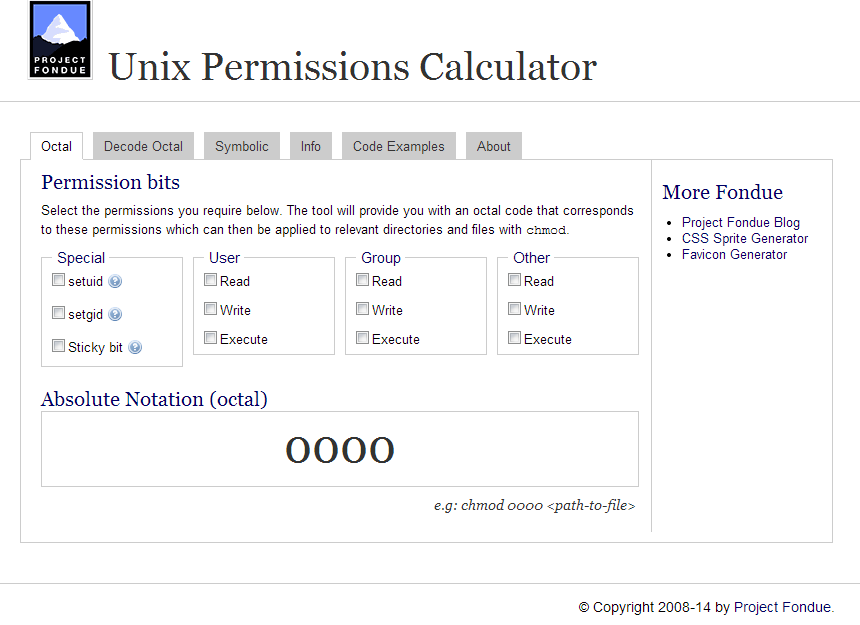
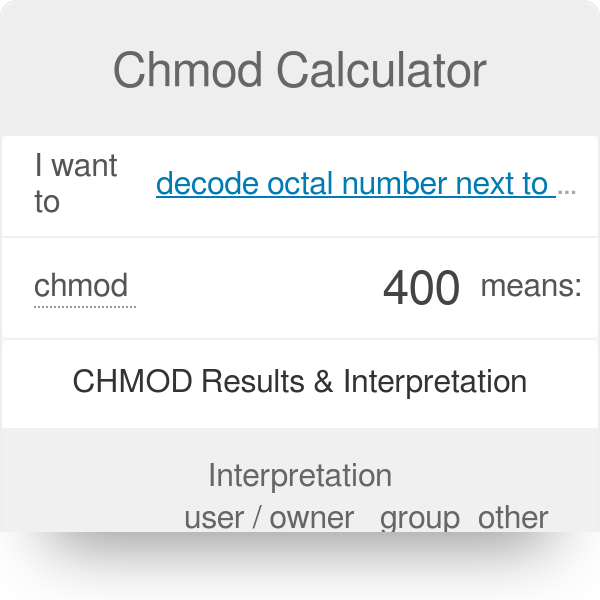
Chmod Numbers

Chmod 700

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Unix Permissions
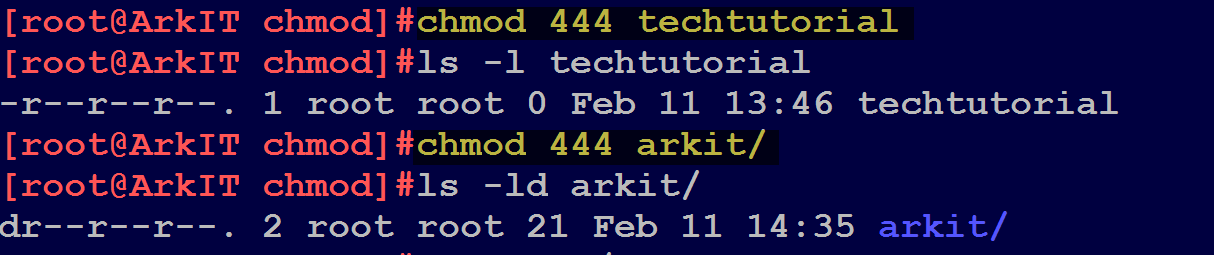
Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
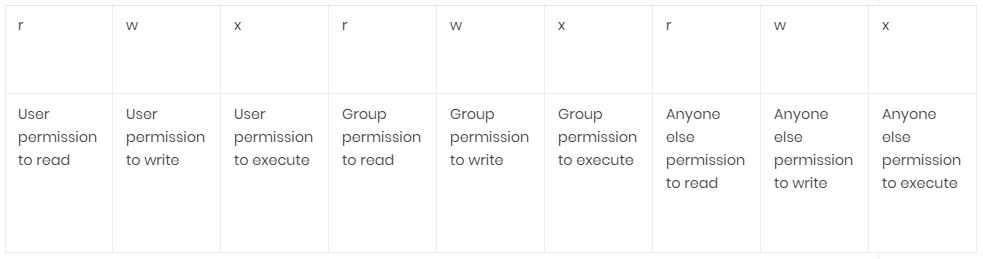
Linux Permissions Explained Linux Hint
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsuqrd7yr237u Am8msiqf70j96klzxefjagdqqwjyc32uhwnrw Usqp Cau

File Permissions Operating Systems I Ppt Download

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
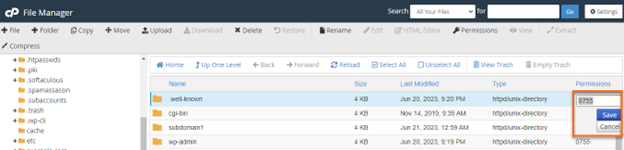
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

File Permission Meanings Stack Overflow

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
Ectzbrjpkaoq7m

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
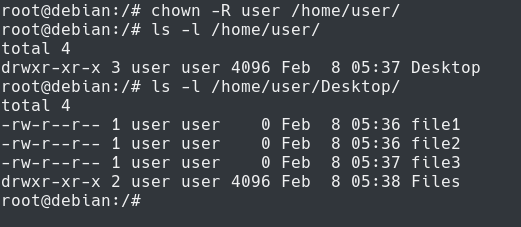
How To Chown Recursively On Linux Devconnected
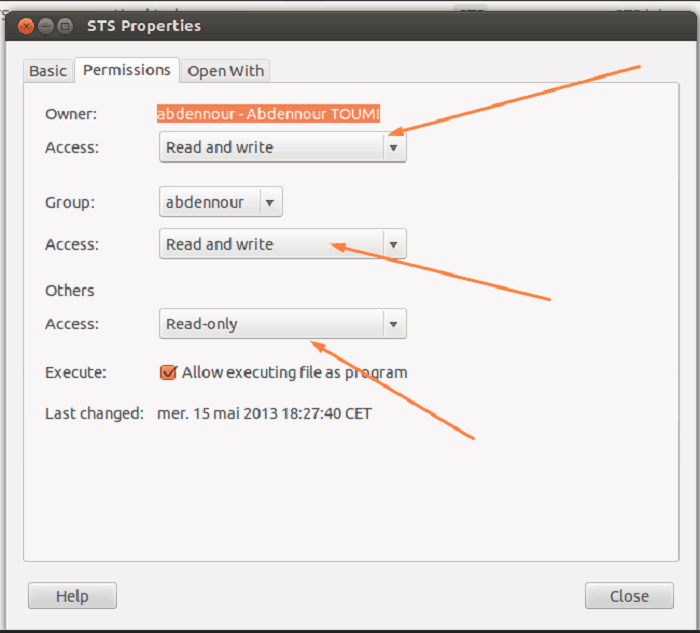
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
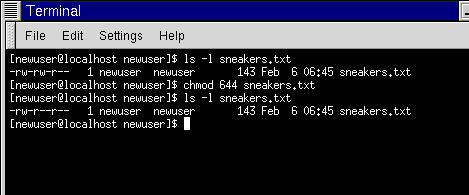
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Understanding File Permissions
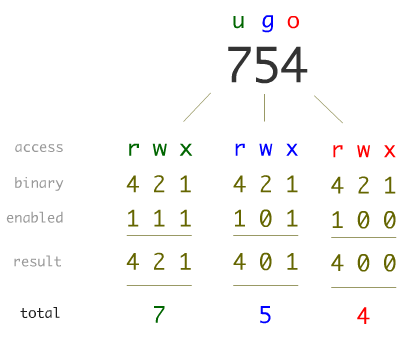
Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
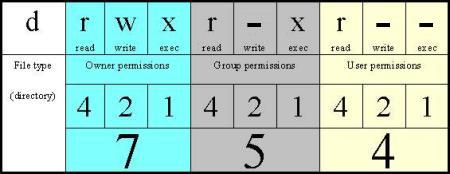
Linux File And Directory Permissions Explained

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
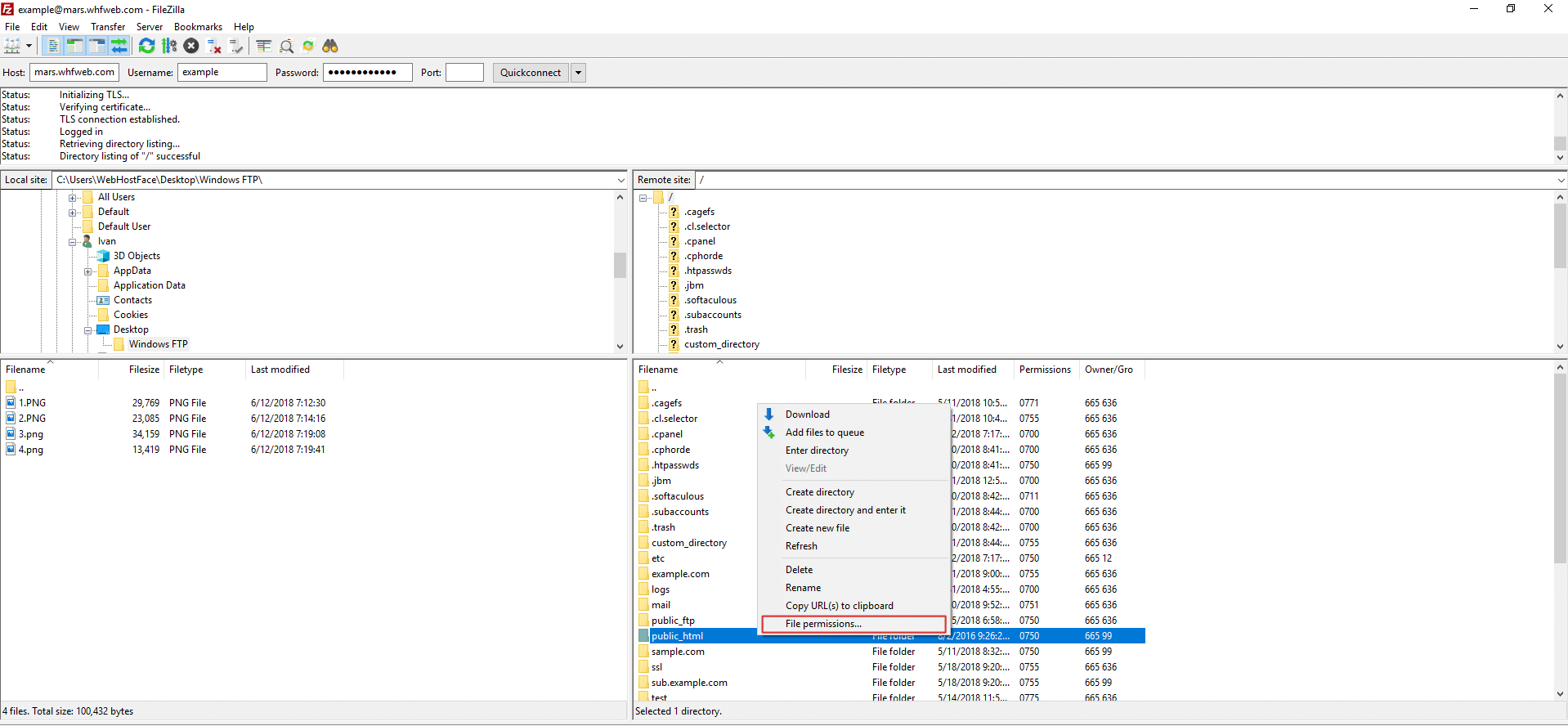
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer

File Permissions Operating Systems I Ppt Download

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
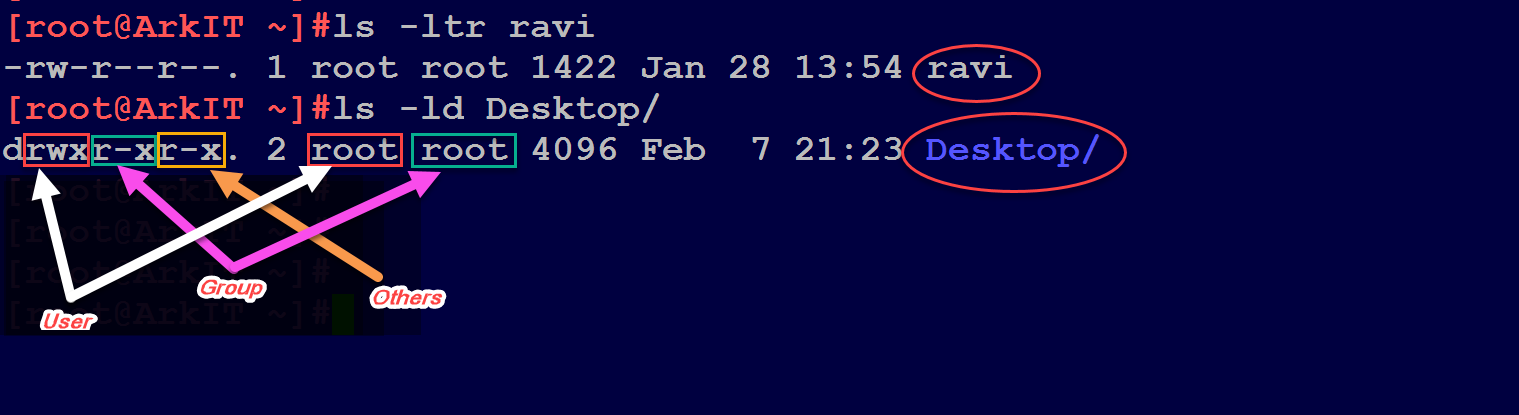
Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Ownership And Permissions

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

14 Permission And Modification Times



