Chmod Example

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Detailed Linux Permissions Command Chmod Modify Permissions Programmer Sought
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux System Rights Management Programmer Sought

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
See also oct if all you have is a string.
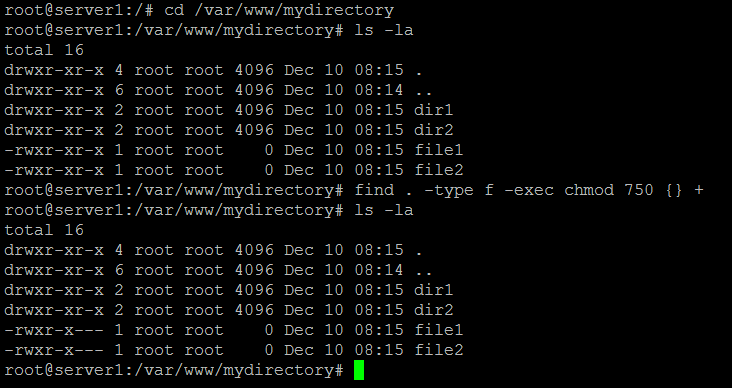
Chmod example. -type f -exec chmod 640 {} \;. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www/html directory to 755 you would use:.
Chmod +hrs sysfile sets the hidden, read-only, and system attributes for sysfile. Sudo chmod -R 755 Example The command gives read, write, and execute privileges to the owner (7) and read and execute access to everyone else (55). The first element of the list must be the numeric mode, which should probably be an octal number, and which definitely should not be a string of octal digits:.
Below is an example syntax of how to use the chmod comamnd…. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others. After you have assigned the executable permissions to the script, you can run the script without bash command as shown.
The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be expressed as:. Let’s say you are currently in the root directory of your Unix-like system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and sub-directories present inside that folder. Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it:.
For files and find. -rw-r--r-- 1 john john 272 Mar 17 08:22 test.txt. Example 9) Assign execute permission to directories only.
To turn on read, write, and execute permissions, and turn off the set-user-ID bit, set-group-ID bit, and sticky bit attributes. $ chmod a-x myscript.sh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a):. Deny execute permission to everyone.
It is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod:. Chmod command examples Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file. The syntax is the rule and format of how the chmod command can be used… the systax options can be reordered.
—xr-xrwx 1 nikhil group users 0 Nov 29 06:02 file1.txt. Now if I use file1.txt in my case, to change ownership I will use the following syntax:. Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a three-digit number.
$ chmod u+x samplescript.sh. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. $ chmod go+rw sample.txt Make a shell script executable by the user/owner.
Chmod -R o-r *.page Numerical Shorthand. $ chmod a-x sample.txt Allow read permission to everyone. Chmod a=rwx file turns on read, write, and execute permissions, and turns off the hidden, archive, and system attributes.
-type d -exec chmod 750 {} \;. Chown - To change owner, change the user and/or group ownership of each given File to a new Owner. Following are few examples on how to use the symbolic representation on chmod.
Give read, write and execute permissions to everyone. Following are some examples:. Changes the permissions of a list of files.
Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode:. To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below. The chmod() function changes permissions of the specified file.
+ symbol means adding permission. Chmod +x myfile - Gives everyone execute permission on myfile. For example, to change file permissions of a file file1.txt, to say rw-r--r--execute:.
Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIX-like operating system. You can vote up the ones you like or vote down the ones you don't like, and go to the original project or source file by following the links above each example. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits.
Chmod -R o-w dirname. This can be done as follows:. Below are examples of making changes to permissions:.
EXAMPLES chmod -w nowrite makes file nowrite read-only. The mode can also be specified using the symbolic method:. Add single permission to a file/directory Changing permission to a single set.
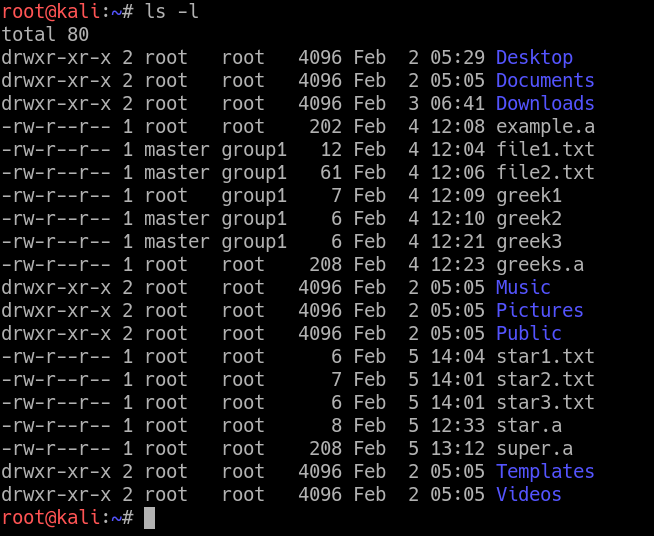
Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:. For example, to set file permissions of file2.txt to be the same as those of file1.txt run the command:. Chown root:root ./test-dir/ Note that you can cross verify the owner and group change for a directory using the stat command - the UID and GID fields in the output display user and group names.
Let’s change the assgn1_client.c permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it. The following are 30 code examples for showing how to use os.chmod().These examples are extracted from open source projects. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions.
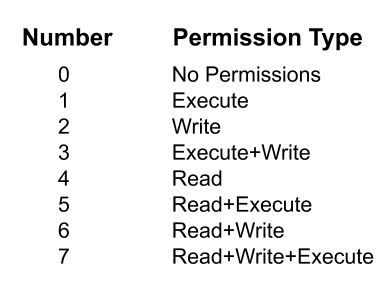
From one to four octal digits Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. # chmod LIST. The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner.
The following chmod command modifies the mock file, example.txt, so that the owner (user) as well other users (group, other) receive writing and reading rights:. And the basic permissions that can be given include read (r), write. How to use chmod command to change file permissions.
For example in my case, the output clearly showed the changed user group ownership. In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. To remove write permission from orgcht:.
You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once. Returns the number of files successfully changed. Chmod g-w mydir chmod o-w mydir chmod g+x mydir chmod o+x mydir.
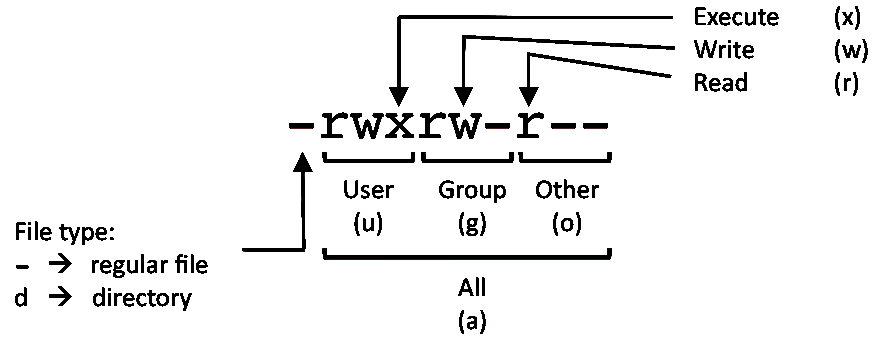
Chmod -R 755 /var/www/html. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma). Permissions can be given to a user who owns the file (u = user), group of said user (g = group), everyone else (o = others) or all users (a).
# alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's .bashrc file for permanent changes. $ chmod a+r sample.txt Make a file readable and writable by the group and others. 0644 is okay, but "0644" is not.
Now, suppose the task is to add execute permission for owner/user, remove write permission but add execute permission to group, and remove all permissions from others. Examples Deny execute permission to everyone:. This is equivalent to the command sequence:.
Chown can also change the ownership of a file to match the user/group of an existing reference file. Chmod ugo+x myfile - Same as the above command, but specifically specifies user, group and other. But a straight format must be followed.,.
$ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/data.php. Following is a sample of ls -l command output. Read, write and execute:.
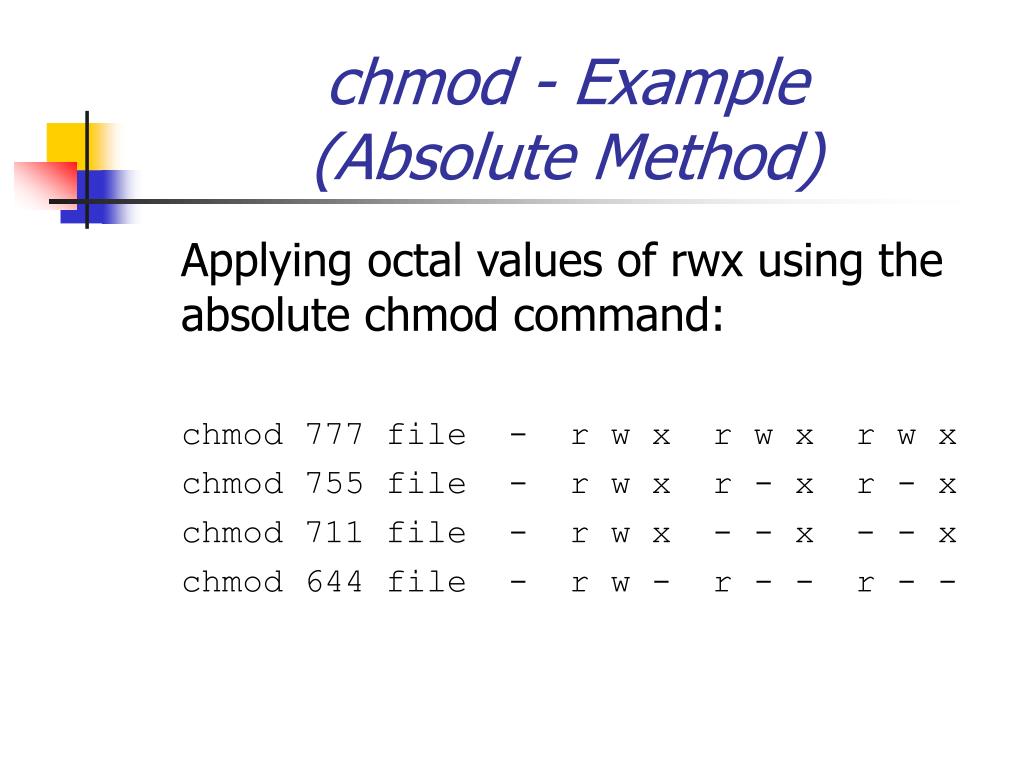
For this example command, we are going to remove the read permission from the other permission group for a file called nowrite. 4+2+1=7 $ chmod 777 sample.sh In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number. For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:.
Do not change the permissions for the group, or for others. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:. $ chmod u+x hello_script.sh Step 5:.
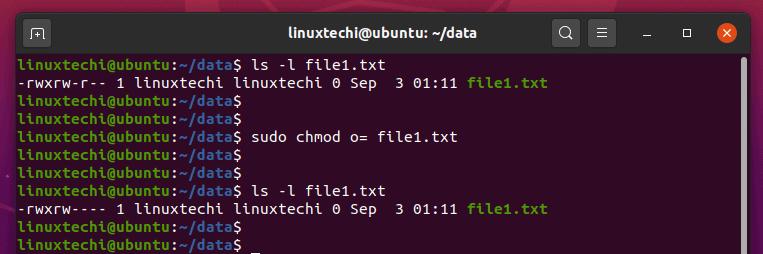
Let’s give Read and Write permission to User/Owner using chmod command. Breaking down this command, we start by using the letter o to specify that we want to modify the Other permission group. Complete Digital Server Solutions For All.
In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users. If you want to change the permission of a file then you need to first find the current permission of the file and then change it to the required permission. Assume that if you are user named user1 and you want to change ownership to root.
You can then execute it like this:. This is equivalent to chmod 0777 aprsal:. Following is an example:.
To change owner of the file:. For setting any other permission combination for owner, group & other , pick corresponding value from each column and use with chmod command , for example chmod 264 file , chmod 400 file , chmod 755 file etc. Chmod Examples in Linux / Unix:.
Where the master is another user in the system. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. $ chmod a+rx pager.pl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others:.
755 can be separated as. Examples of Using chmod command Assign permission to a File. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax.
Chmod a+r file Make a file readable and writable by the group and others:. Chmod go-w+x mydir This denies group members and others the permission to create or delete files in mydir (go-w) and allows group members and others to search mydir or use it in a path name (go+x). Remove the execute permission for all users:.
Generally, “site chmod” through ftp has only basic functionality – it’s not the full Linux command, so what you can do with it is extremely limited. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 700 (chmod a+rwx,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. Chmod u+x myfile - Gives the user execute permission on myfile.
To make a script executable use +x or u+x, for example :. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. Chmod u=rw example.jpg Change the permissions for the owner of example.jpg so that the owner may read and write the file.
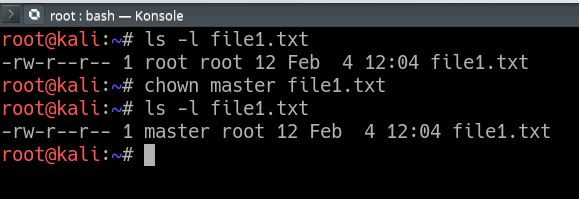
-c--changes Verbosely describe the action for each File whose ownership actually changes. Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, which can be either an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new permissions or a symbolic representation of changes to make, (+-= rwxXstugoa). Here I have a file named file.txt.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 754 (chmod a+rwx,g-w,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. In this example, users who are not the owner of the file and who are not members of the Group (and, thus, are in the Others class) have no permission to access the file. Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions.
To set all permission bits on (anyone can read/write/execute):. Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation. $ chmod u=rw,g=r,o= birthday.cgi In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group:.
$ chmod ugo+rw example.txt Referencing all the user classes (a) is a possible alternative:. For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone:. The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permission.
Repulsively remove the write permission for other users:. $ sudo chmod --reference=file1.txt file2.txt The reference file is file1.txt while file2.txt is the file that will take up the file permissions for the reference file. Chmod octal value file-name.
Now, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file. Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod u+x myscript.sh. This is illustrated in the calculation below.
Chmod a-x file Allow read permission to everyone:. In the example above, the permission is defined using the octal/numerical mode (755). We can give multiple permissions to a file at the same time or in one command by using the below syntax:.
Just like the way you do it for files. Chmod is Linux command used to change file permissions.chmod changes user, group and other read, write and execute permission.chmod 755 is popular use case for chmod .chmod 755 is generally used to make most of the operations without problem because it provides ease for system administrators while running applications. The chmod command can be used in a couple of different ways, with permissions (or modes) set by numbers or by letters.

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
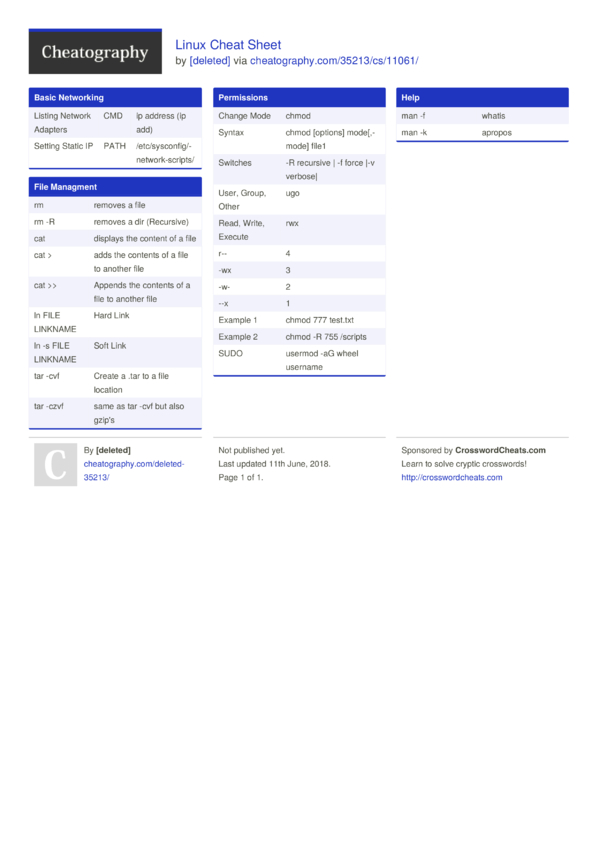
Linux Cheat Sheet By Deleted Download Free From Cheatography Cheatography Com Cheat Sheets For Every Occasion

How To Change Permissions Folder And All Its Subfolders And Files In Linux

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

人気ダウンロード Chmod 777 Example ただの車

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
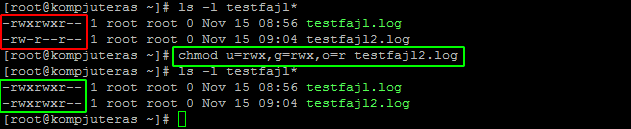
How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Umask Wikipedia
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
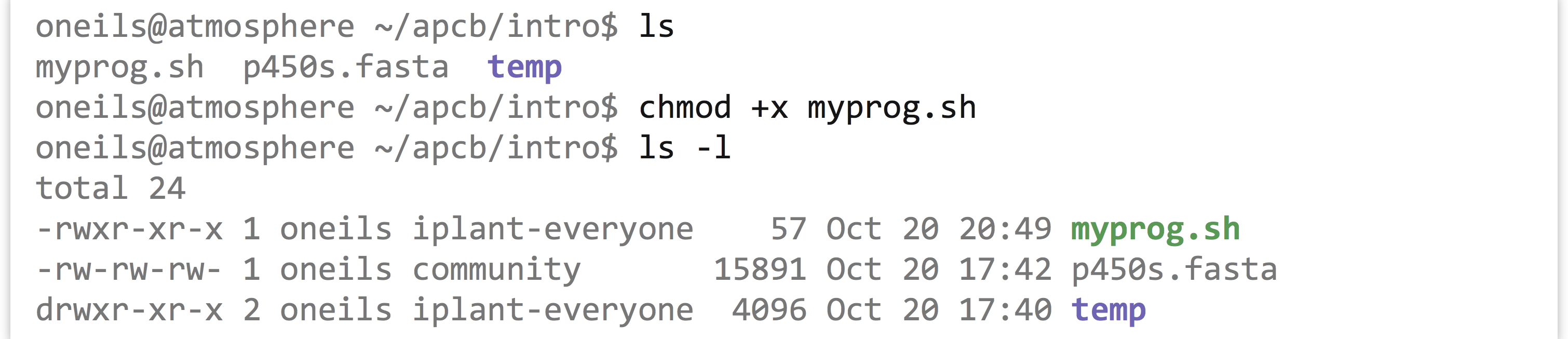
Permissions And Executables A Primer For Computational Biology
Playing With Linux And Sql Chmod Command Usage And Example

What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper

Ownership And Permissions

Magna Cybersec
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students

Filepermissions In Linux

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

How To Hayward Dot Click

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat

Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base
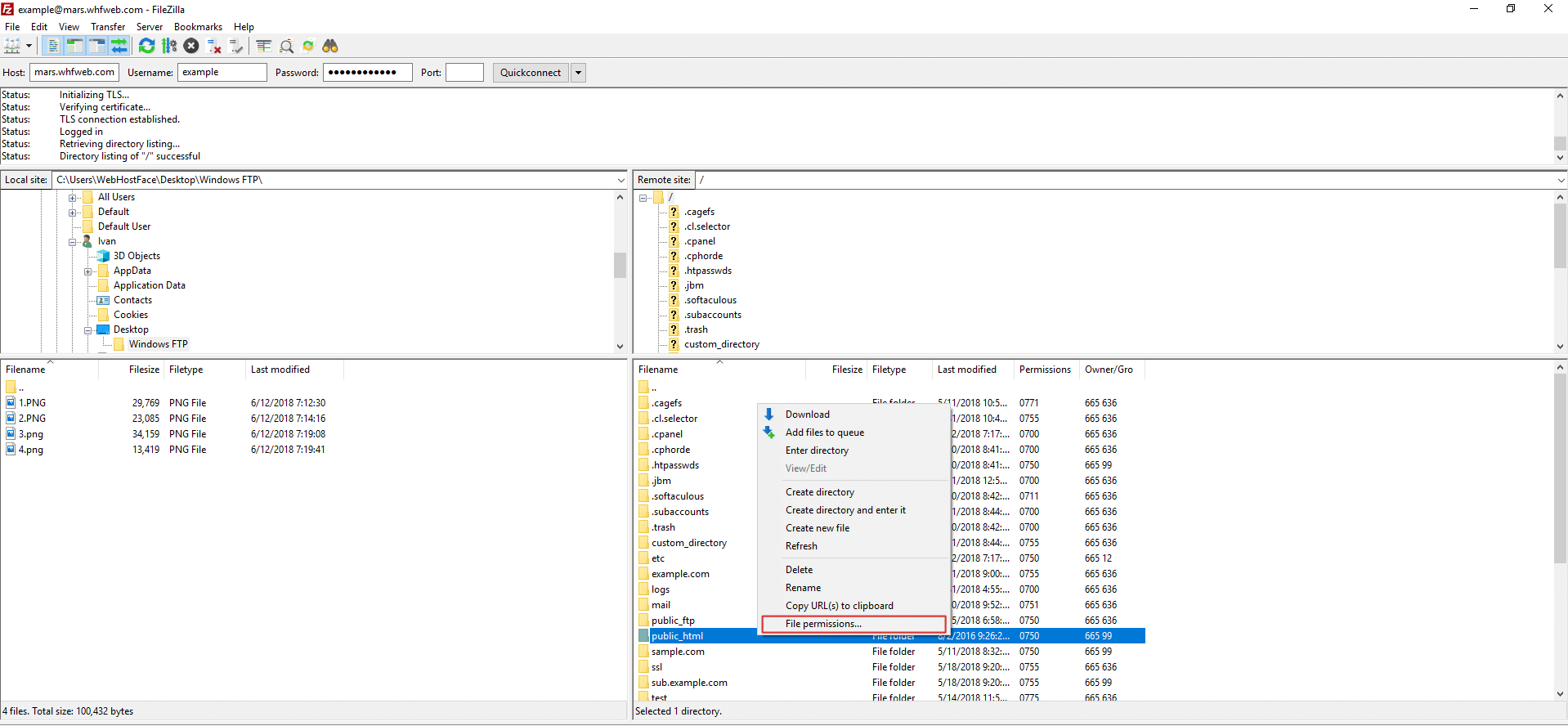
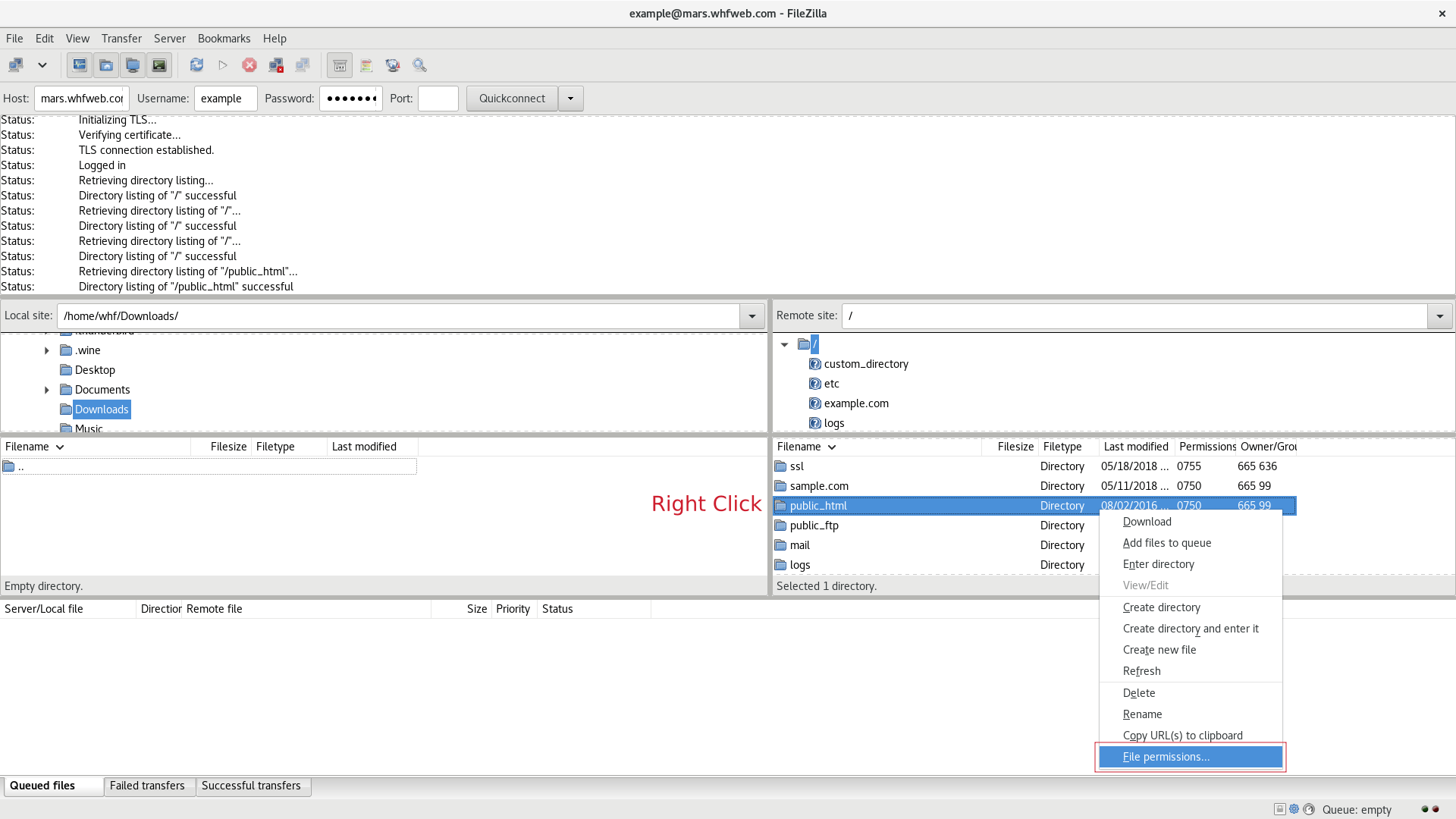
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
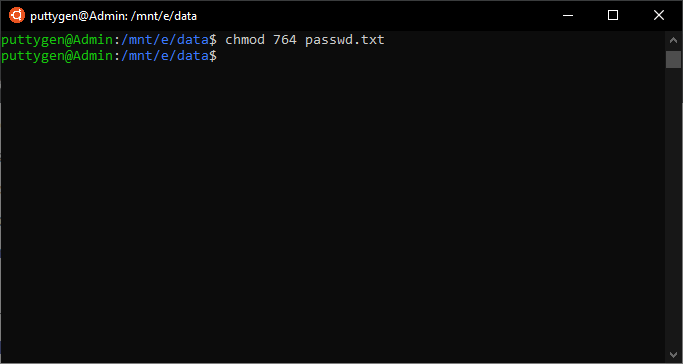
Top 50 Linux Commands With Example
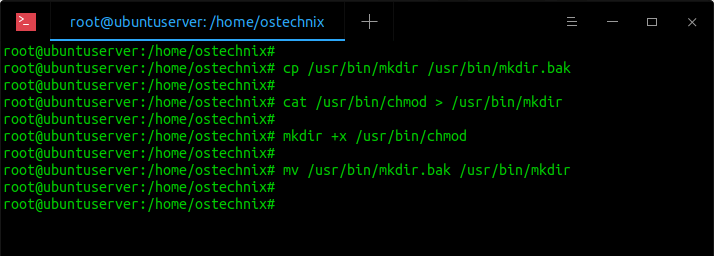
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux

Solved Shell Questions 6 Points Each 1 What Is Short C Chegg Com

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command
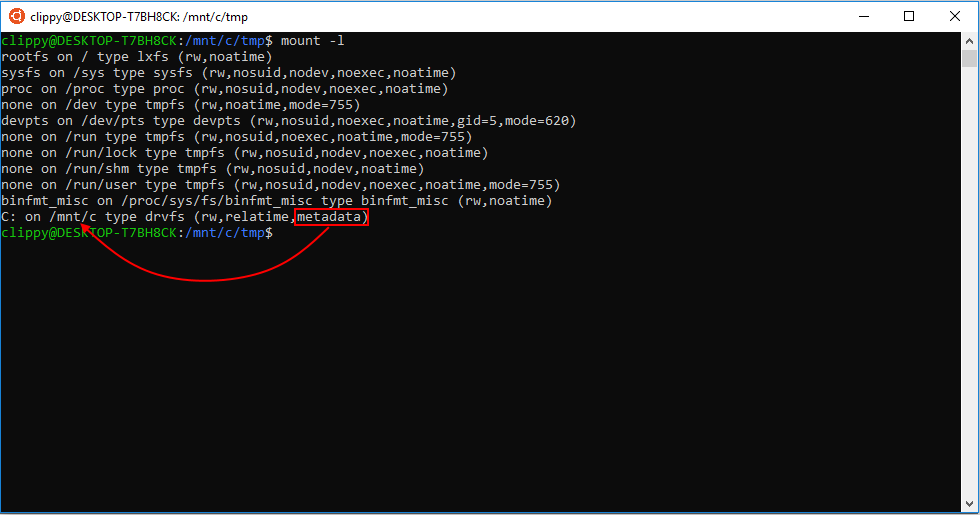
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu

Solved Outcome Unix And Your First Program 1 The Comman Chegg Com
Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Understanding Permissions Jetapps

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Extropia Tutorials Introduction To Unix For Web Technicians The Chmod Utility

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Unix Tutorial Five

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Basic Chmod Examples
Linux Command Cheat Sheet

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Umask Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

How To Make Bash Script Executable Using Chmod
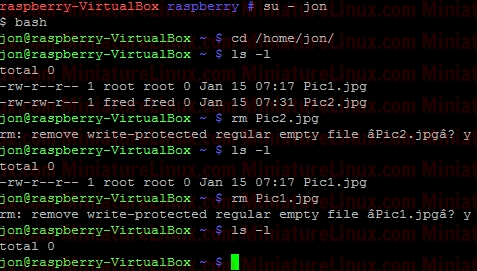
Linux Examples Users And Groups

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod Wikipedia
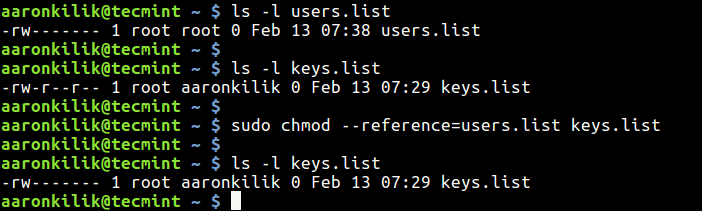
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
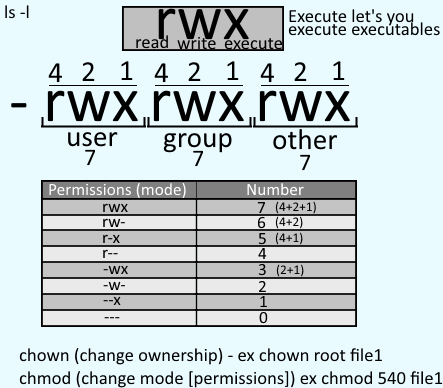
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions
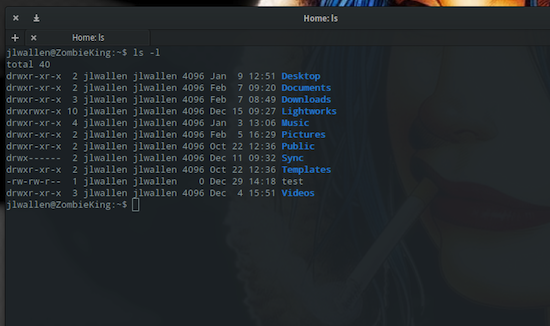
Getting To Know Linux File Permissions Linux Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
Can T Chmod Files Operation Not Permitted Ixsystems Community

Common Bash Commands

Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach

Chmod Dictionary Definition Chmod Defined

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

1 File Permissions Look At Permissions With Ls L Output Rw R R 1 Enda Users 1234 Jun 2 10 51 File Ext Ppt Download

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

A Complete Guide To Chmod Recursive Force And More

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions
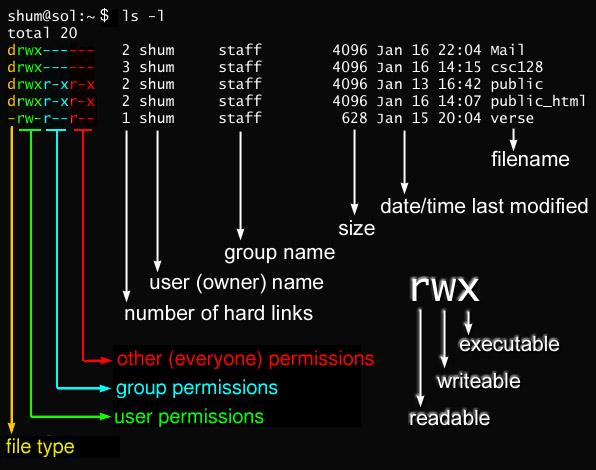
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau
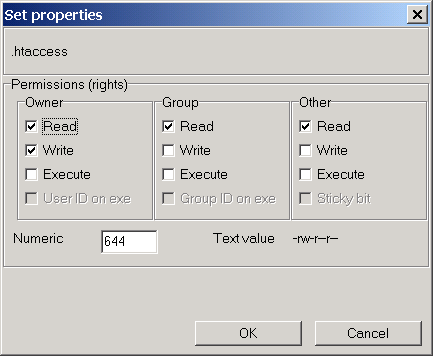
Chmod Help

Linux Linux File Permissions And Directory Configuration Programmer Sought

Linux Free Course Module 3 Chapter 1 File Management File Attributes Permissions

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

06 Users Groups And Permissions

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders



