Chmod Linux Permissions

Linux Chmod Chown The File Folder Access Control Me Learning Tech
Video Linux File Permissions Chmod And Chown Linux Org
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmtof5oge8os R2lzc9s8y8xkmcm3kyhtt M Kqujtci7flb3h Usqp Cau

How To Modify The File S And Directories Permission In Linux Vasanth Blog

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
= turns on the specified permissions and turns off all others.

Chmod linux permissions. Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters. This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directory. There are two ways to use the chmod command:.
Set the permissions for a file or directory by using the chmod command. The possible values are:. File permission can be represented in a symbolic or numeric (octal) format.
To read, write and execute. (O)thers can read, can write and can't execute. Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to ch ange the permissions (or access mod e) of a file or directory.
In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 555 (chmod a+rwx,u-w,g-w,o-w) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.
Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits. Linux permissions dictate 3 things you may do with a file, read, write and execute. Change file permissions in Linux.
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. If you want to use an option, you have to place it right after the chmod/chown command. Using chmod with Absolute Permissions.
Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command. In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command. We can use the ' chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'.
Each row has 2 examples, one for setting that permission for a file, and one for a directory named ‘dir’. Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and the world. Chmod -R a-x+X publicDocs.
+ turns on a permission. The default Linux security model is a bit inflexible. $ find /home/user/demo -type f -print.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. In Linux, the file is associated with an owner and a group and assigned with permission access rights for three different classes of users:. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma).
Use the chmod command to set file permissions. Sets GID, sets read, write, and execute permissions for user, and sets read and execute permissions for Group and Others:. To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following:.
If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Chmod Modifies File Permissions. 9 Comments Originally posted October 13, 14.
In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. In short, “chmod 777” means making. The chmod command lets you change the permissions for a Linux file.
The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file. Chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions. This is a dangerous permission to have on any file and you should avoid using it.
In Linux, files and directories are treated similarly. This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories. Set the permission of file.txt to "read and write by everyone.".
The owner can read, write and execute. The permission part of a symbolic mode is any combination of the following:. I would like to change permissions of a folder and all its sub folders and files in one step (command) in Linux.
Chown -R 755. In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions. Linux File Permissions, chmod, & umask.
Others(everybody else) File permissions can be changed. For more information about file permissions, see “Umask Command in Linux”. On all files and directories in personalStuff) adds read, write, and special execution permissions for user, removes read, write, and execution permissions for Group, and removes read and execution permissions for Others:.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories. The chmod command uses a three-digit code as an argument.
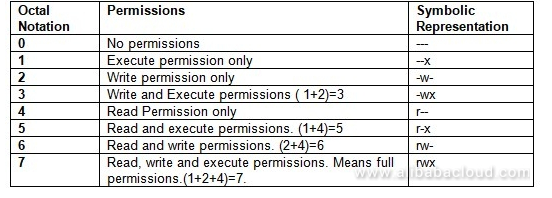
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify. The first number represents the Owner permission;. Here are some command chmod commands with their explanation:.
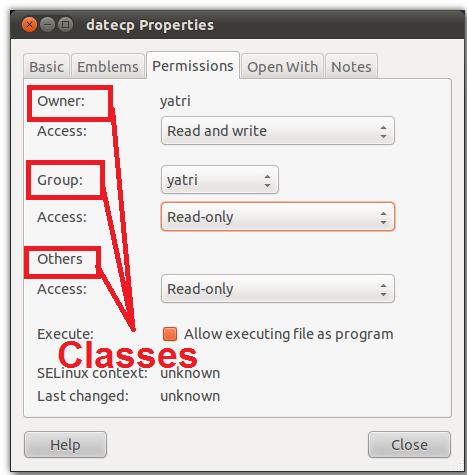
Owner, group, and everyone. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. File permissions in Linux file system are managed in three distinct user classes:.
By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is -R (Recursive). How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command.
The command is relatively simple to use and involves using. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person.
Therefore, full permissions for everyone on the system would look like:-rwxrwxrwx. And the last number represents the permissions for all other. I have already tried the below command but it works only for the mentioned folder:.
The main difference between access rights for files and directories is that the x permission on a file grants permission to execute it, where on a directory, it grants permission to enter it. Bash, Shell, Terminal, Command Line cheat sheets linux Ubuntu. Checking through the graphical interface or using the command.
Linux grants three different types of permissions — read, write, and execute — for three different scopes:. Linux is a multi-user system, and access to the files is controlled through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. In this example, you are setting permission to 0755:.
Before explaining the syntax of the chmod command, you need to look at the cryptic way Linux reports file permissions. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. Chmod 775 file_name chmod ug+rwx,o=rx file_name Both the commands give all permissions (code=7) to user and group, read and execute (code=5) for others.
In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. The name speaks for itself.
Now when these permissions are applied to a file, they are applied in levels. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
All three of these are pretty self-explanatory. -turns off a permission. There are three sets of permissions.
Each class can have read, write and execute permissions. Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively. If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command.
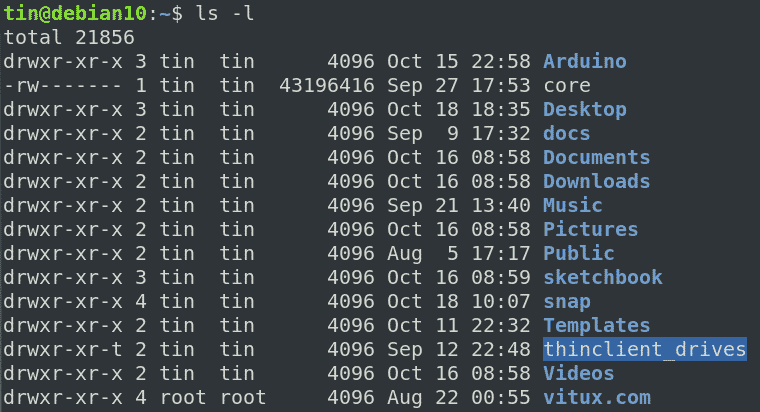
Permissions used to be called mode of access and hence chmod was the short form of change the mode of access. Following is a sample of ls -l command output. With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros.
Find out how default permissions for new files are configured via a user's umask value. Using letters is easier to understand for most people. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. Chmod -R u+rwX,g-rwx,o-rx personalStuff:. There are two options to choose from, depending on your personal preference:.
Chmod 766 (chmod a+rwx,g-x,o-x) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. Linux File Permissions #. There are 2 ways to use the command -.
Common chmod commands and their meaning. Check Permissions using GUI. See this to help create these, if you wish I will cover using chmod.
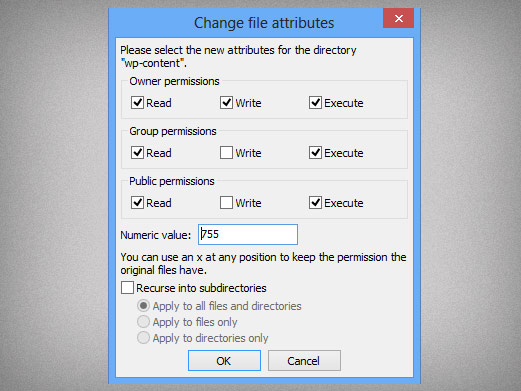
In this tutorial, we look at the chmod. The chmod command stands for “change mode”, and allows changing permissions of files and folders, also known as “modes” in UNIX. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod.
Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. Multi-user systems, such as Linux, require setting up and managing file permissions that ensure only authorized users have access to files they are supposed to. Setting File Permissions in Command Line.
There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. Chmod permissions path chmod has permission arguments that are made up of 3 components. Changing permissions of 'cfdna_hc_bam.bam':.
You can use chmod command for changing the permissions on a file in Linux. Linux Permissions & Levels In Linux, there are basically three permissions that you will normally have to worry about:. How to View Check Permissions in Linux To start with file permissions, you have to find the current Linux permission settings.
Chmod +rwx filename to add permissions. Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around on the file system) Each digit of this code sets permissions for. User/owner, group and others/public.
Read, write and execute. To find all files in /home/user/demo directory, enter:. Accomplishes the same thing as the above command, using symbolic notation.
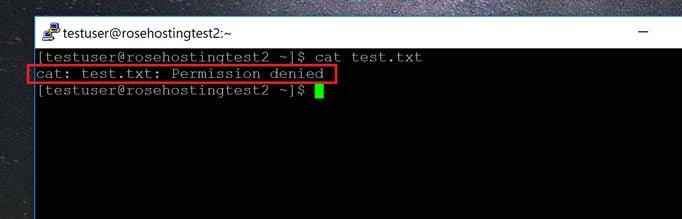
It asks for my password, I provide it and the Results:. When I enter cd , ls -l, to see the permissions on the directory in which my file is, this is the result. This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permission of files and directories.
In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. The op part of a symbolic mode is an operator that tells chmod to turn the permissions on or off. (G)roup can read, can write and can't execute.
They are referred to in Linux by a single letter each. Chmod 775 /opt/lampp/htdocs Is there a way to set chmod 755 for /opt/lampp/htdocs and all of its content including subfolders and files?. A sample permission string would be chmod 640 file1, which means that the owner has read and write permissions, the group has read permissions, and all other user have no rights to the file.
The chmod command can accept numeric integers, such as 0664, which relate to user permissions. Chmod +x filename.sh to make filename.sh executable. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions.
This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories. This means that owner, group and everyone has the all the rights i.e. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Take a look at this example:. Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories. If you want an easy way to know the Linux file permission in numeric or symbolic mode, you can use this chmod calculator.
R read - you may view the contents of the file. The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories. Understand how Ubuntu / Linux file permissions and special mode bits work.
There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions. Linux File Permission :. The chown command stands for “change owner”, and allows changing the owner of a given file or folder, which can be a user and a group.
$ chmod -R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command. The second represents the Group permissions;. Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set.
Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order:. Chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions.
Set the permissions of file.cgi to "read, write, and execute by owner" and "read and execute by the group and everyone else". The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. Sudo chmod 775 cfdna_hc_bam.bam.

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium

Linux Users And Groups Linode

File Security

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

Understanding File Permissions

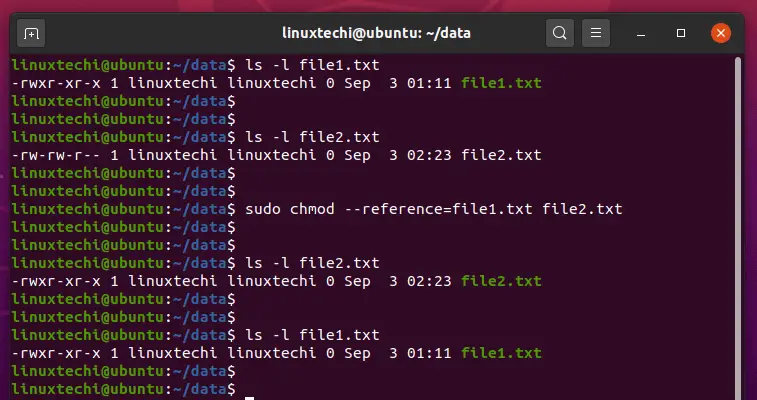
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsacd7mr Ecztzl Lq8wap9enfi2vj2xlffbqx6amvc25tn3 R6 Usqp Cau

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Sep Towards Data Science

Chmod 7777

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Unix Permissions

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
%20access%20permission%20%EC%98%88)%20chmod%20644%20test.jpg)
Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Whatever You Knew About Chmod Is Wrong Alien Coders

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Managing Linux Permissions

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Linux Permissions Pluralsight
What Is Chmod 777

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Kirelos Blog
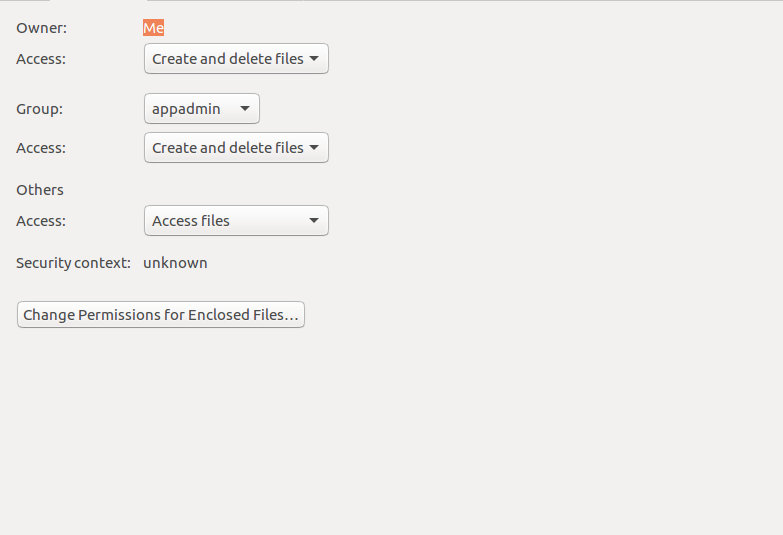
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator By Chmodcalcu Issuu

Give Permissions In Ubuntu Itechzo Give Permissions In Ubuntu

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
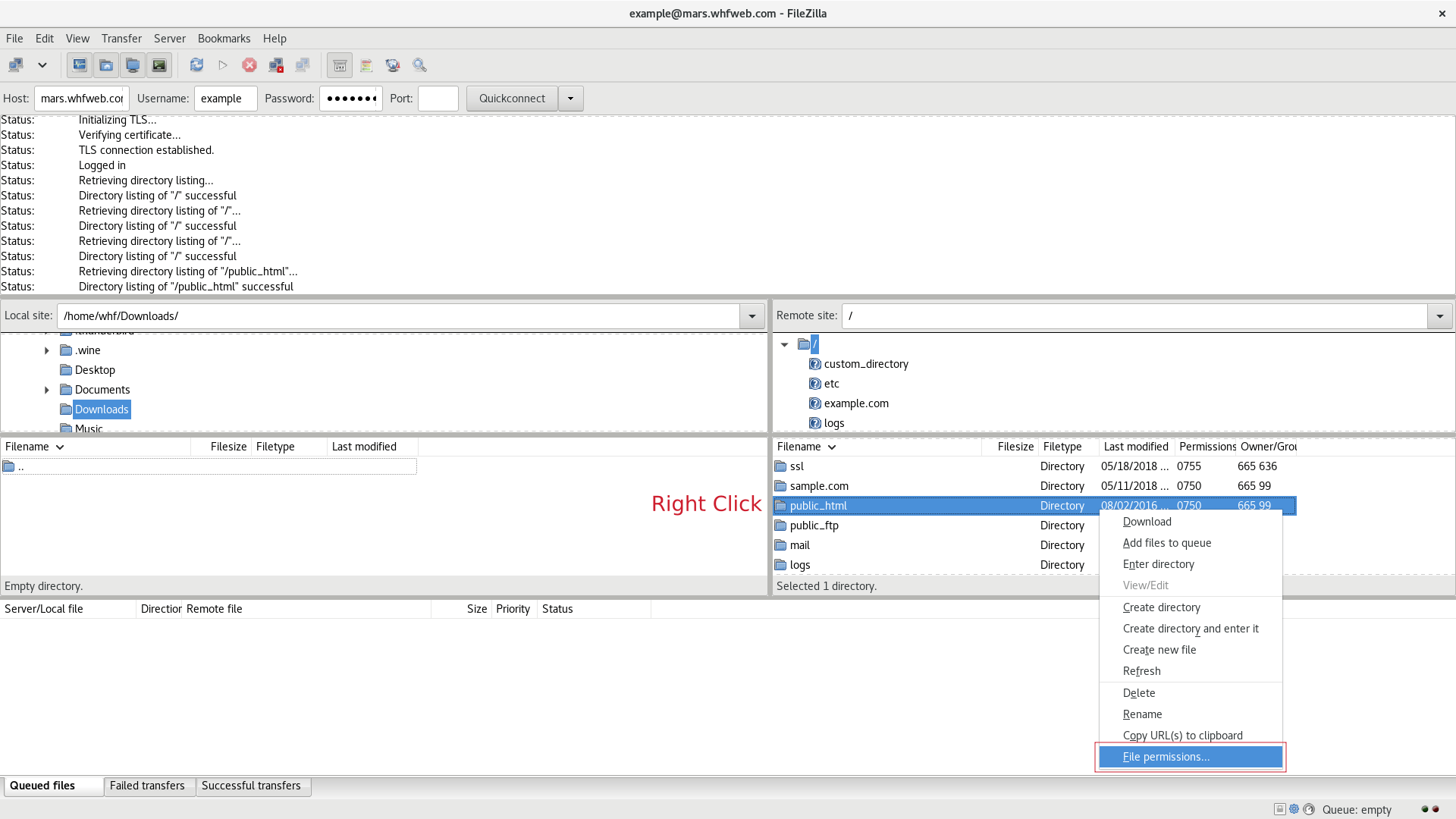
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube
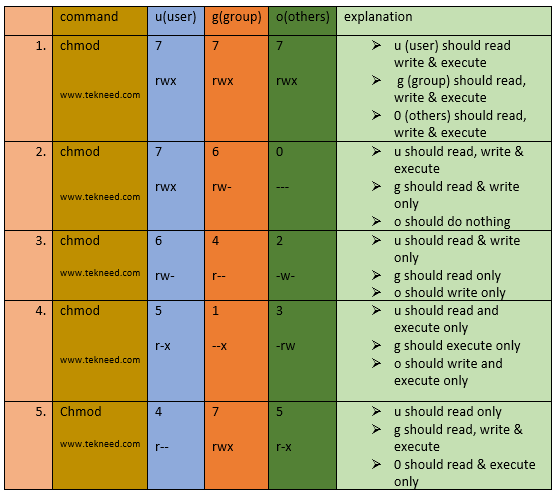
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Ownership And Permissions

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Designlinux

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Chmod Wikipedia

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
Linux Chmod Tips

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls
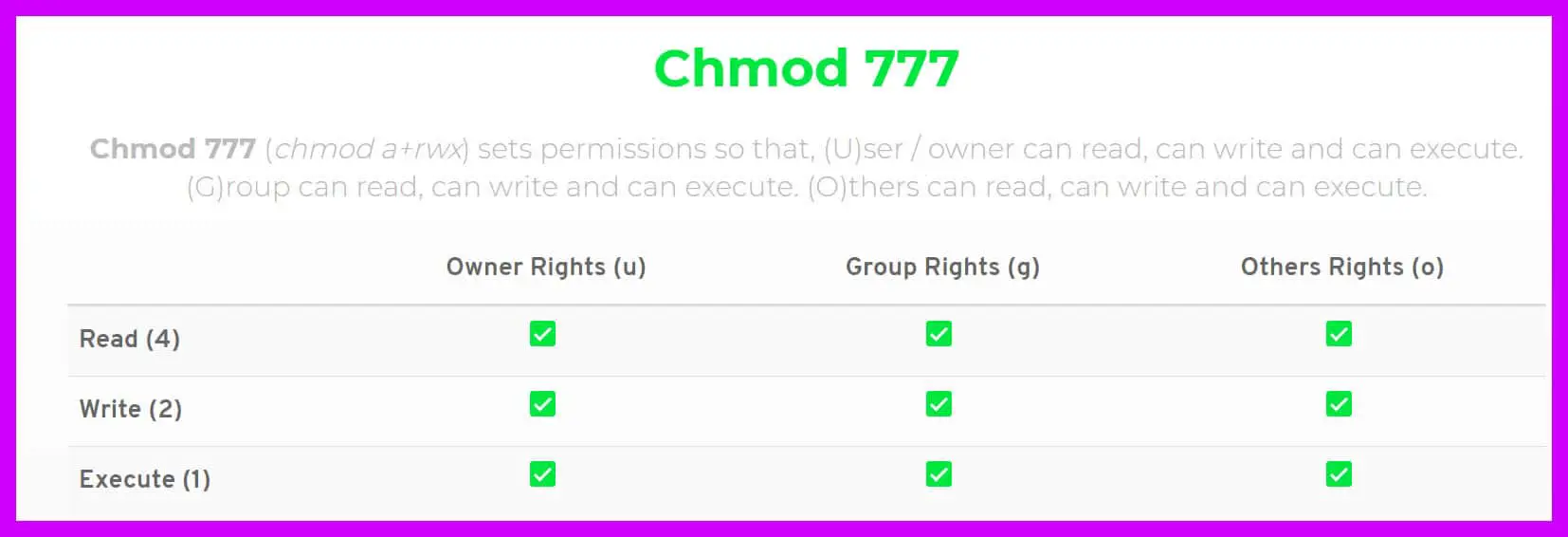
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions



