Chmod Command In Linux To Give All Permissions

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
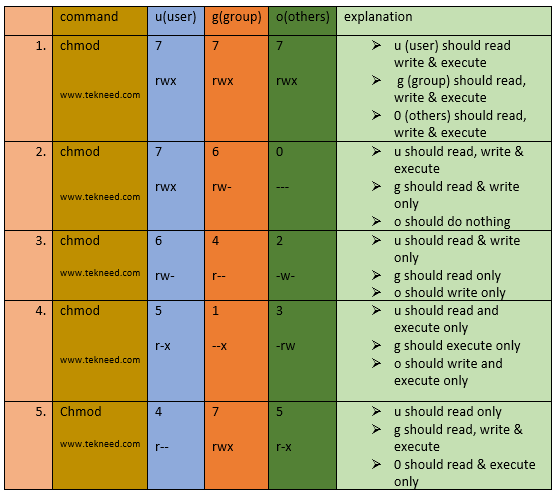
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1
$ find /home/user/demo -type f -print.

Chmod command in linux to give all permissions. Repulsively remove the write permission for other users:. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. There are 2 ways to use the command -.
I actually give group write permissions as well, for users which need to modify content, such as users used to deploy code. Where FILENAME is the name of the file. Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and the world.
Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode:. I don't want to use chmod ugo+w filename. More Information on.
This was tested on CentOS 5.5. To better understand how the chmod command works, it’s prudent that we study the Linux file. Below is a list of numerical permissions that can be set for the user, group, and everyone else on the.
Chmod command is followed by which level user i.e. Use chmod -R 755 /opt/lampp/htdocs if you want to change permissions of all files and directories at once. With chmod command, you can use following set of permissions, to apply desired conditions on a file/directory.
$ sudo find /path/to/Dir -type f -print0 | xargs -0 sudo chmod 644. Chmod Modifies File Permissions. Read, write and execute:.
Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file. Now that you understand the actual permissions of files, it’s time to learn how to change those permissions. You can set the sticky bit permission to file1 with the following command:.
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories. The modes include permissions and special modes.
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. The symbolic method and the absolute form. The syntax of chmod command is chmod options mode filename THe important options are:.
You can do the same in symbolic mode. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. And even this… chmod 775 file_name chmod ug+rwx,o=rx file_name Both the commands give all permissions (code=7) to user and group, read and execute (code=5) for others.
Chmod -R o-w dirname. Remove the execute permission for all users:. The chmod command, short for change mode is used to manage file and directory permissions and determines who can access them.
Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it:. You can also set the sticky bit permission to file so that only the file owner the root user can delete the file. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma).
Chmod has two operating modes:. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone.
The chmod command can be used with octals (as. Here, I have given 7 methods. Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples.
$ chmod -R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command.
Who – ugoa controls :. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. Give the file’s owner read and write permissions and only read permissions to group members and all other users:.
For example, give full access to the directory permission recursively with all sub-directories and files:. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. That looks like this:.
You can use the find command. The basic syntax is:. Chmod +w testfile.txt running ls -l testfile.txt prints-rw-rw-r-- 1 ravi ravi Mar 10 18:09 testfile.txt but in case of +r and +x it works properly.
We either have to be running as root, or have privileges to run chown through sudo:. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. 4+2+1=7 $ chmod 777 sample.sh.
Permissions can be given to a user who owns the file (u = user), group of said user (g = group), everyone else (o = others) or all users (a). Following are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode:. The chmod command (change mode) is a shell command in Linux.
File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. We can use the ' chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'. Read,write,execute permissions for all other users.
With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros. Here are some examples of how to use the chmod command in numeric mode:. Below is the command's general structure:.
How do I give permission to a folder in Linux?. Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. If no references are specified it defaults to “all”.
In this example, you are setting permission to 0755:. Chmod is the command used to change the permissions of an object, and is short for “CHange MODe”. The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. R = Read w = Write x = Execute. Changing Access Permissions with chmod.
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options. Remove the execute permission for all users:. To change file and directory permissions, use the command chmod (change mode).
How to Use the chmod Command in Linux Command Syntax. See this to help create these, if you wish. When I run chmod +w filename it doesn't give write permission to other, it just gives write permission to user and group.
In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. Give the file’s owner read, write and execute permissions, read and execute permissions to group members and no permissions to all other users:. Chmod command understanding how-to grant file permissions why i said title like that, because chmod command used for changing file mode bits.
Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory. Let’s now dive in and explore the nature of file & directory permissions and how they can be modified. R w – r – – – – x so read-write the owner, r for the group and execute for the others.
To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal. Each shell script must have the execute permission. The chmod command can accept numeric integers, such as 0664, which relate to user permissions.
We will only provide related value to the command. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:.
$ chmod 700 executable Give All Permissions To All Roles. Verbose Chmod Examples in Linux / Unix:. This is done with the chmod command.
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. Sudo chown alice:alice document.docx 5. User, group or all.
Chmod -R o-w dirname. Give read, write and execute permissions to everyone. To change all the directories to 755 (drwxr-xr-x):.
Please remember we removed the executable permission of chmod command only, but not other commands' permission. Only the object owner, superuser or root account can change the permissions of a file/folder. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
So, if you want to give a file 664 permissions, you’d issue the chmod command like this:. There are a few ways to restore the execute permission to chmod. Method 1 - Copy contents of chmod binary to other working binaries.
Use find /opt/lampp/htdocs -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person.
The chmod command can be used in a couple of different ways, with permissions (or modes) set by numbers or by letters. To remove the write permission for other users:. Read,write,execute permissions for the owner of the file.
If the number of files you are using is very large. In this post, i will share with you the basic chmod command usage to change linux file permission. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux.
The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. Chmod -R 777 permissions. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
After executing this command. In Linux, as a regular user, it’s not possible to give away the ownership of our files to someone else. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all).
After user level we have provide what needs to be done i.e. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, using the find command and a pipe we can target just files or just folders as in the following examples.
What permissions will the following command give :. Use chmod 755 $(find /path/to/base/dir -type d) otherwise. Read,write,execute permissions for the group owner of the file.
Answer Setting permissions to 641 is equivalent to the following permissions :. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. Recursively change the permissions of a directory.
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. To give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it:. The owner of a file can change the permissions for user (u), group (g), or others (o) by adding (+) or subtracting (-) the read, write, and execute permissions.
Chmod -R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. We can give all permission to all roles which means user, group and others can read, write and execute.
Mode can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new. In my previous blog post I discussed how Linux file permissions work, and now I am going to discuss how to change permissions using chmod. It can change file system modes of files and directories.
Both the codes give read (code=4) permission to user, write and execute (code=3) for group and read and execute (code=5) for others. There are three sets of permissions. On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it.
The below character references are used with chmod command to identify the Linux users/Linux groups/world (other Linux users) to whom the new permissions apply. U = Owner g = Users in the Group o = Other users not in the group a = All users/Everyone. The Linux chmod command can be used to change the existing permissions on a file.
In this example we only want the user to read , write, and execute permissions and others not. And the basic permissions that can be given include read (r), write. These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed.
This is very insecure and dangerous. Chmod is command which changes permission of a file or folder for particular user or group as per instructions provided. To find all files in /home/user/demo directory, enter:.

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Ownership And Permissions

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

File Permissions Rhel 7 Tutorial

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
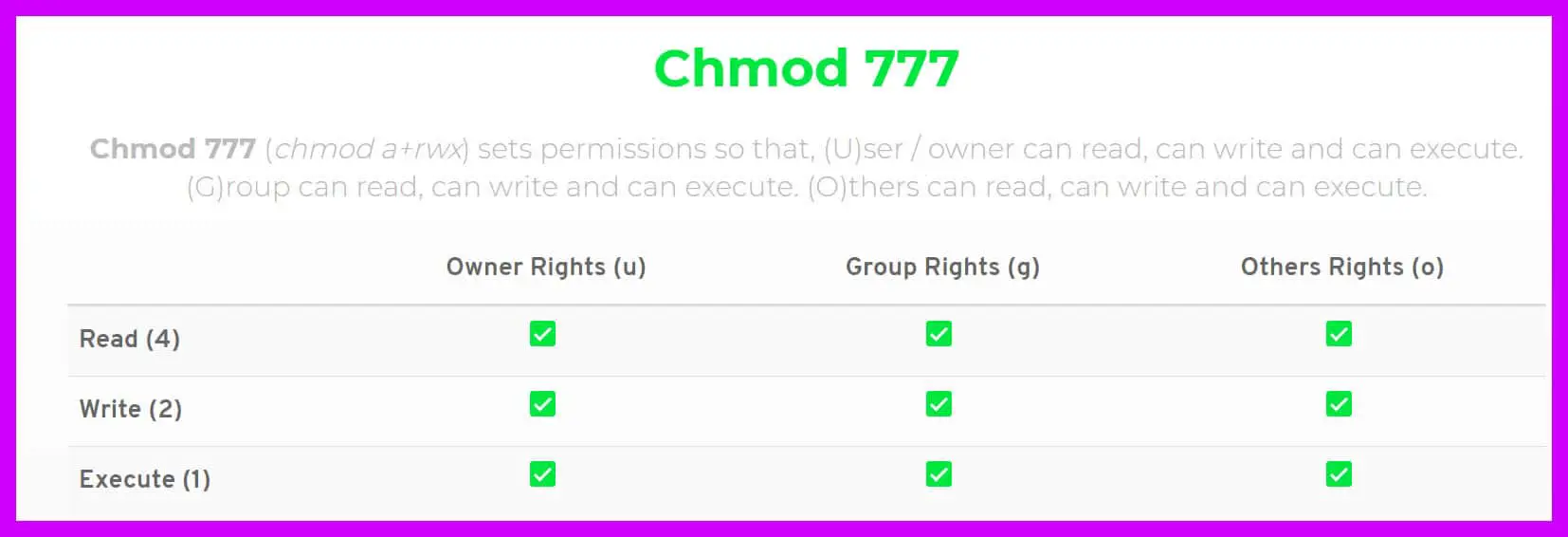
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Understanding File Permissions

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

File Security

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth

For It Professionals Linux Command
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Special Permissions Access Control Filesystem Attributes In Linux Study Com

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
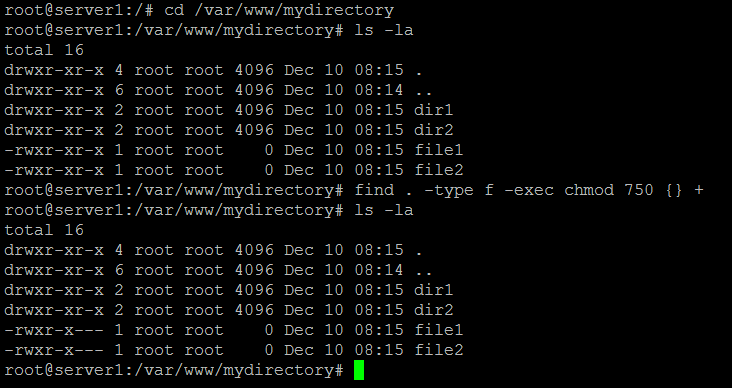
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu

File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions For Beginners

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
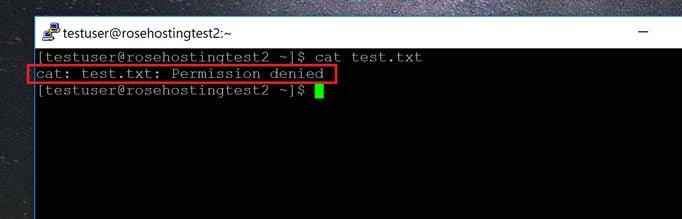
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets
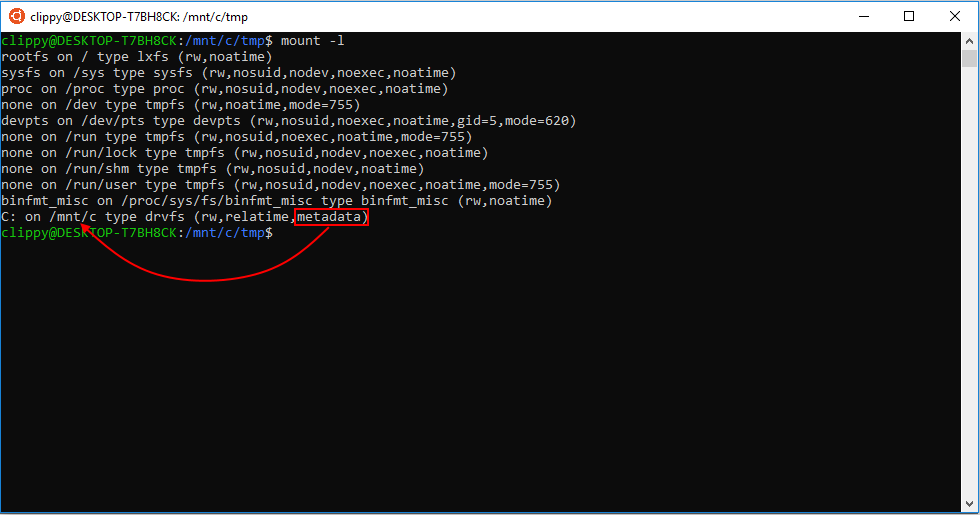
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
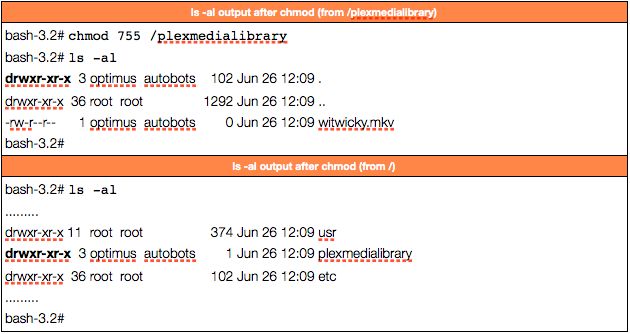
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

14 Permission And Modification Times
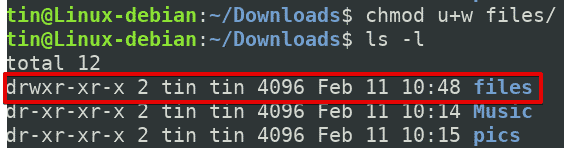
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Give Write Access Chmod Command

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
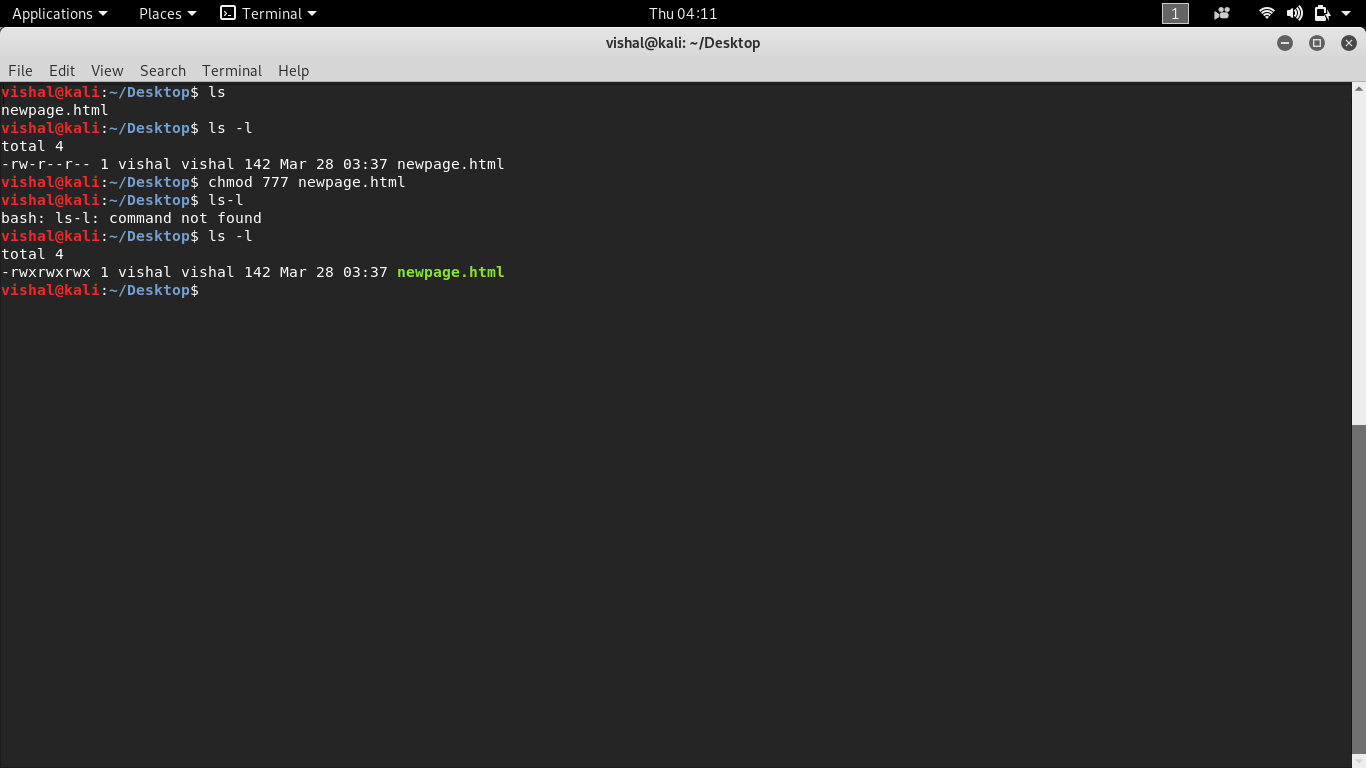
Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Reset Website File Permissions From Command Line Vi Wickam Online Expert
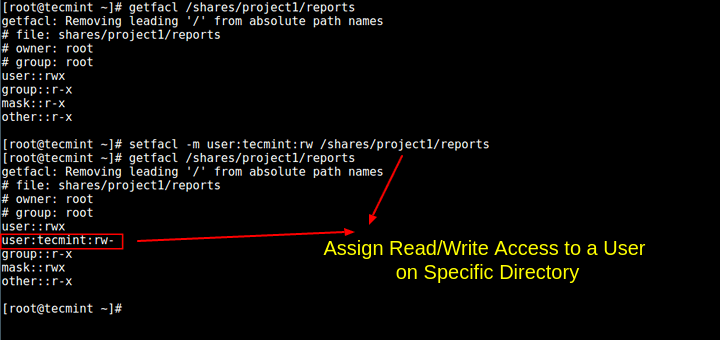
Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Chmod Wikipedia
1

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

Linux Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
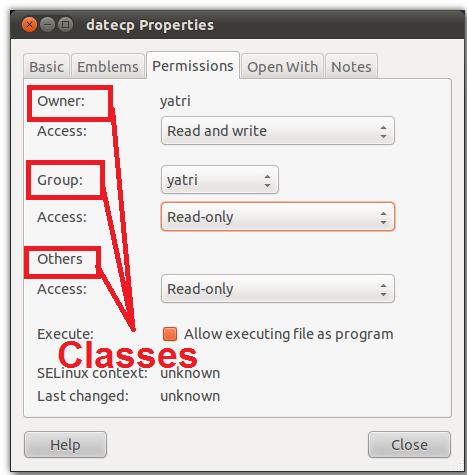
What Is Chmod 777
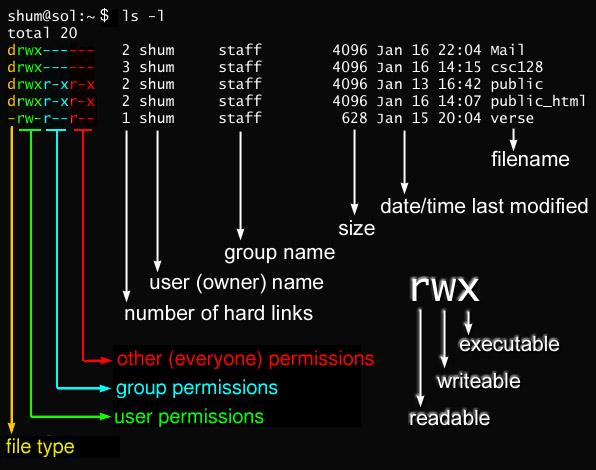
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Chmod Command In Linux Linux Cppsecrets Com

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux
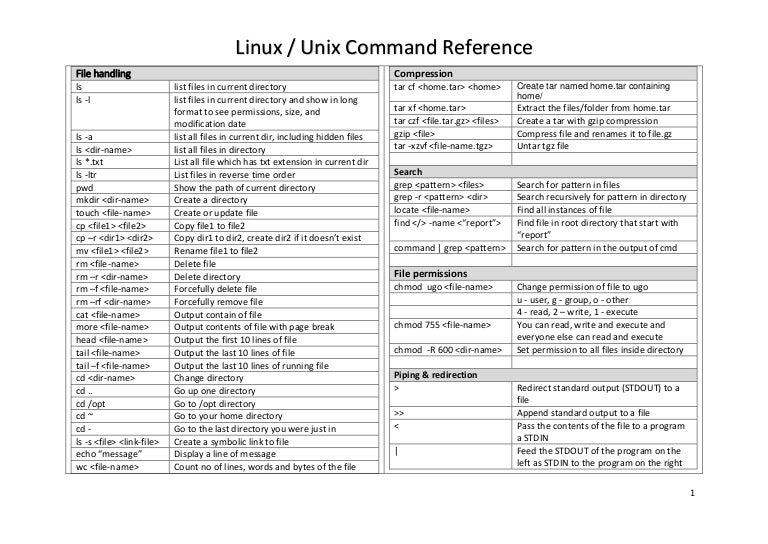
Unix Linux Command Reference

Unix Permissions

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Project Ii Six Task Management System Linux File Permissions Programmer Sought

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
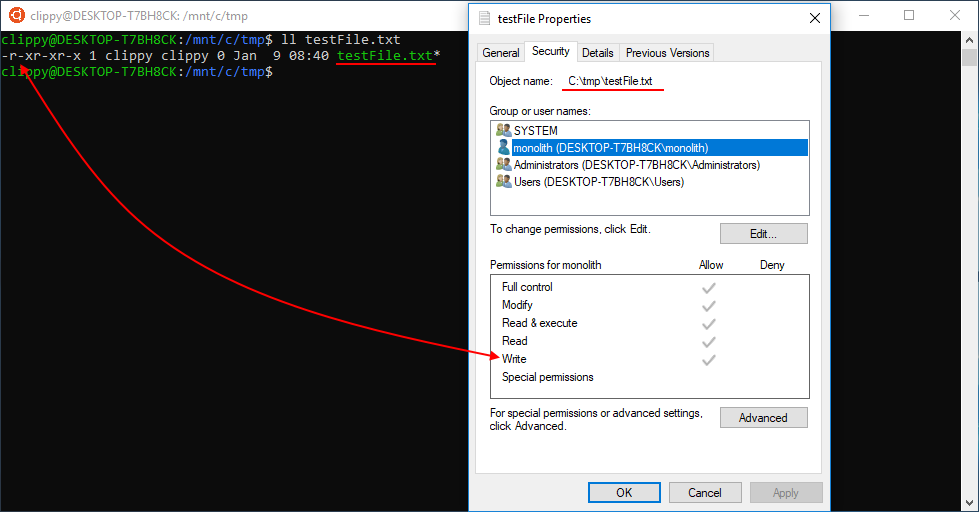
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission



